Spring基本介绍
Spring基本介绍
1.官方资料
2.Spring5下载
1.进入官网
2.进入Spring5
3.进入Spring5的github
4.进入Spring5的github
下拉 Access to Binaries, 进入 Spring Framework Artifacts

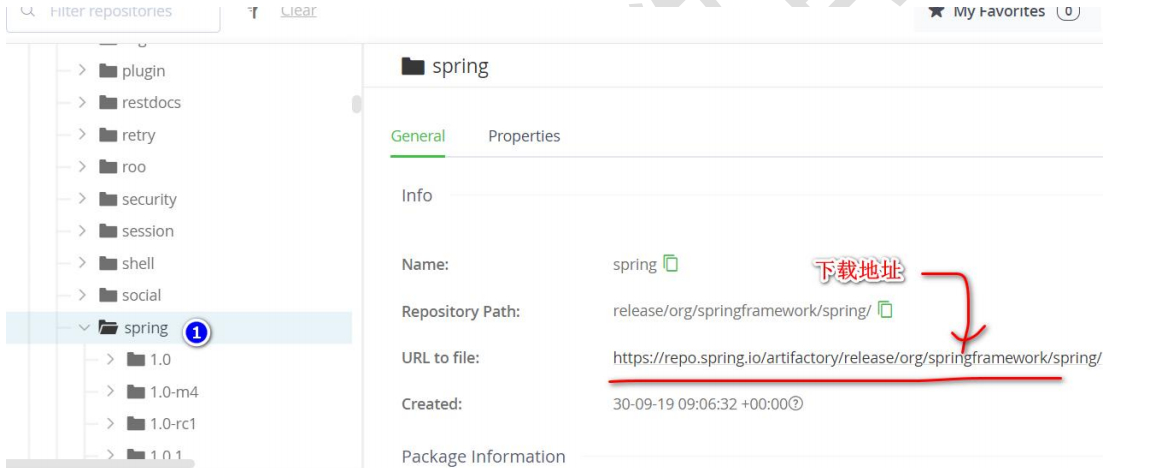
5.在线文档
https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/current/reference/html/
6.Spring 学习的核心内容
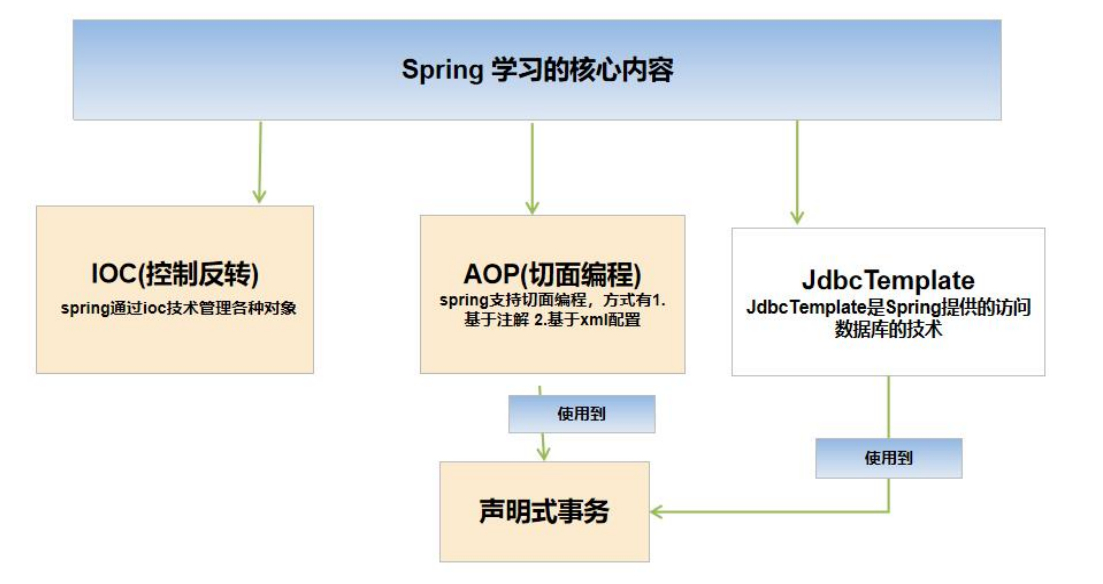
1、Spring 核心学习内容 IOC、AOP, jdbcTemplate, 声明式事务
2、IOC: 控制反转 , 可以管理 java 对象
3、AOP : 切面编程
4、JDBCTemplate : 是 spring 提供一套访问数据库的技术
5、声明式事务: 基于 ioc/aop 实现事务管理
3.Spring 几个重要概念
-
Spring 可以整合其他的框架(Spring 是管理框架的框架)
-
Spring 有两个核心的概念: IOC 和 AOP
-
IOC [Inversion Of Control 反转控制]
● 传统的开发模式[JdbcUtils / 反射]
程序------>环境 //程序读取环境配置,然后自己创建对象.

解读上图(以连接到数据库为例说明)
1.程序员编写程序, 在程序中读取配置信息
2.创建对象, new Object???() // 反射方式
3.使用对象完成任务
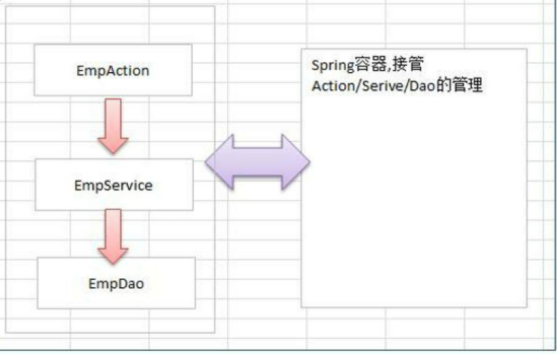
● IOC 的开发模式 [EmpAction EmpService EmpDao Emp]
程序<-----容器 //容器创建好对象,程序直接使用.
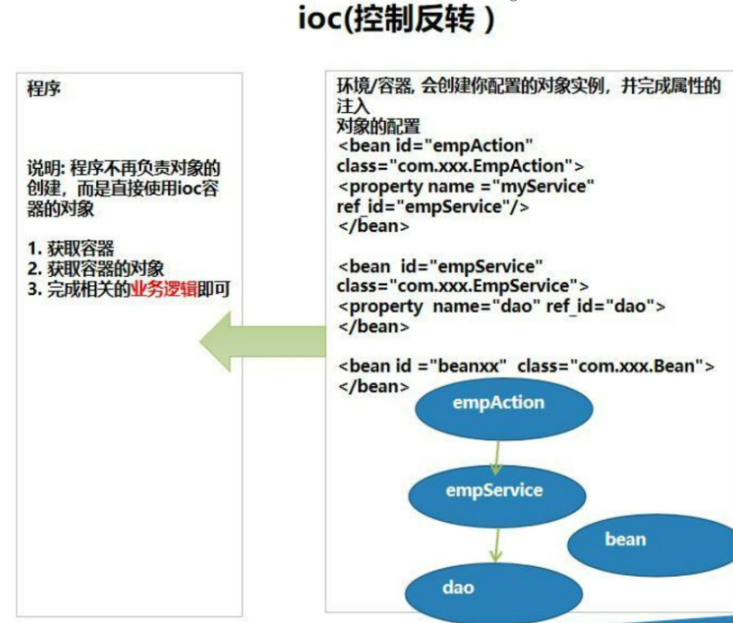
解读上图
1、Spring 根据配置文件 xml/注解, 创建对象, 并放入到容器(ConcurrentHashMap)中,并且可以完成对象之间的依赖
2、当需要使用某个对象实例的时候, 就直接从容器中获取即可
3、程序员可以更加关注如何使用对象完成相应的业务, (以前是 new ... ==> 注解/配置方式)
4、DI—Dependency Injection 依赖注入,可以理解成是 IOC 的另外叫法.
5、Spring 最大的价值,通过配置,给程序提供需要使用的web 层[Servlet(Action/Controller)]/Service/Dao/[JavaBean/entity]对象,这个是核心价值所在,也是 ioc 的具体体现, 实现解耦.
4.Spring 快速入门
1.需求说明
1、通过 Spring 的方式[配置文件],获取 JavaBean: Monster 的对象,并给该的对象属性赋值,输出该对象信息.

2.完成步骤
1、下载Spring5
2、创建 Java 工程:spring5 , 为了清晰 Spring5 的各 jar 包作用
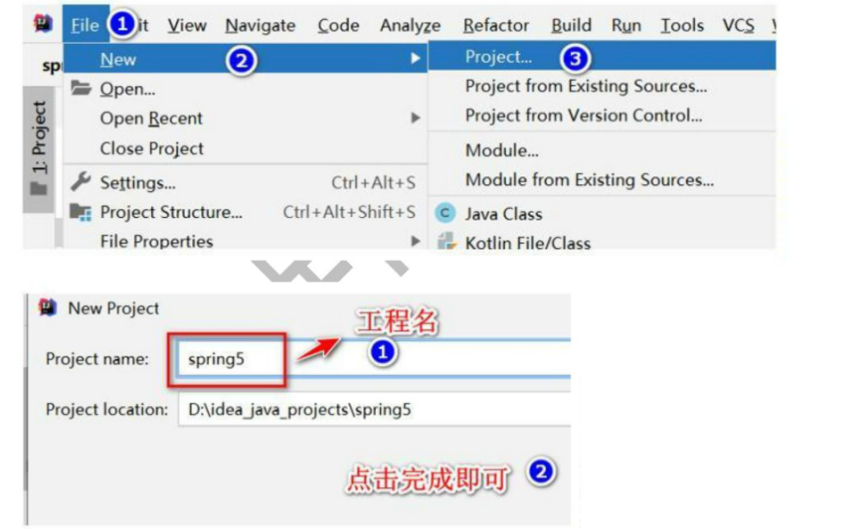
3、引入开发 spring5 的基本包


4、创建代码实现
Monster实体类
public class Monster {
private Integer monsterId;
private String name;
private String skill;
//全参构造器
public Monster(Integer monsterId, String name, String skill) {
this.monsterId = monsterId;
this.name = name;
this.skill = skill;
}
//无参构造器一定要写,Spring反射创建对象时,需要使用
public Monster() {
}
public Integer getMonsterId() {
return monsterId;
}
public void setMonsterId(Integer monsterId) {
this.monsterId = monsterId;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getSkill() {
return skill;
}
public void setSkill(String skill) {
this.skill = skill;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Monster{" +
"monsterId=" + monsterId +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", skill='" + skill + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
创建beans.xml文件
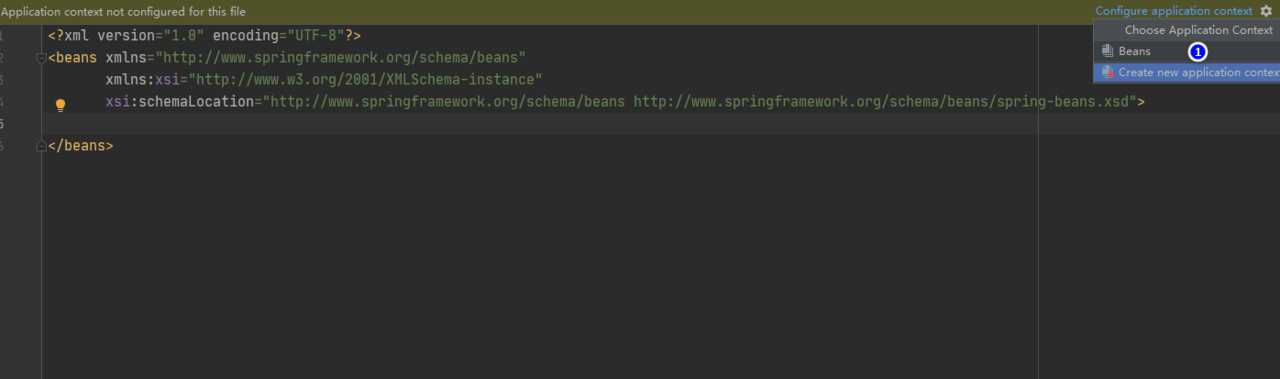
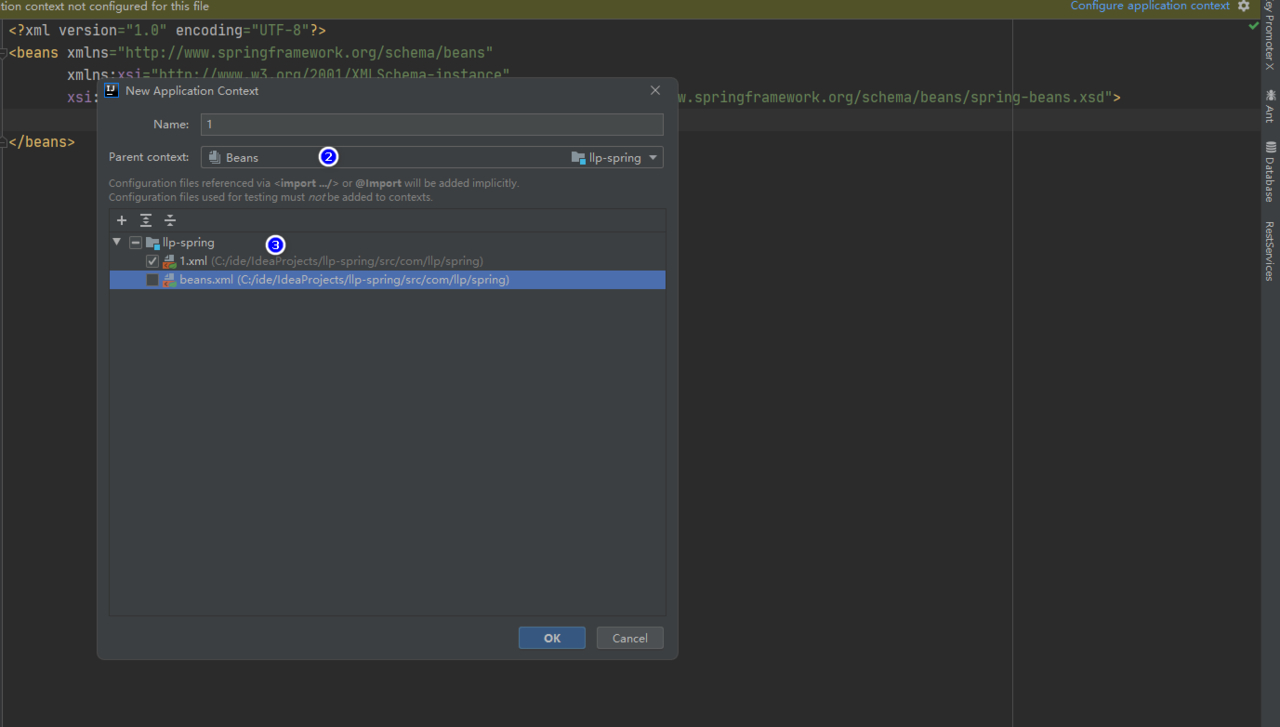
beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--
1. 配置monster对象/javabean
2. 在beans中可以配置多个bean
3. bean表示就是一个java对象
4. class属性是用于指定类的全路径->spring底层使用反射创建
5. id属性表示该java对象在spring容器中的id, 通过id可以获取到对象
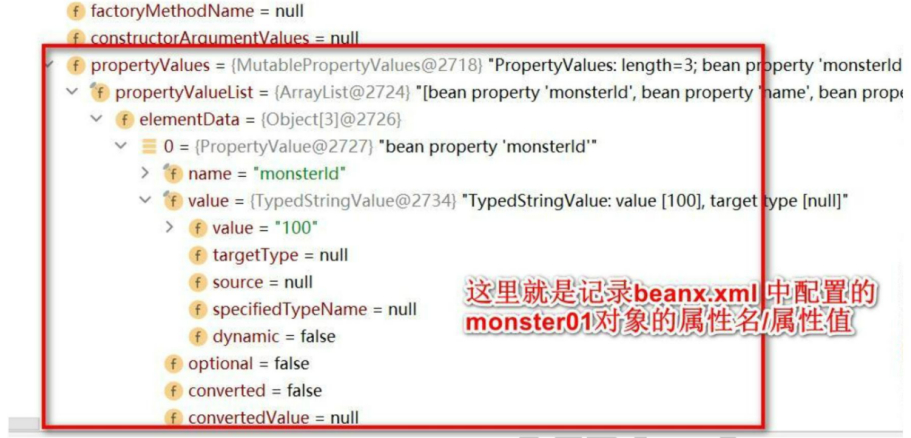
6. <property name="monsterId" value="100"> 用于给该对象的属性赋值
-->
<bean class="com.llp.spring.bean.Monster" id="monster01">
<property name="monsterId" value="1"/>
<property name="name" value="孙悟空"/>
<property name="skill" value="打妖怪"/>
</bean>
<bean class="com.llp.spring.bean.Monster" id="monster02">
<property name="monsterId" value="2"/>
<property name="name" value="牛魔王"/>
<property name="skill" value="野蛮冲撞"/>
</bean>
</beans>
SpringBeansTest
public class SpringBeanTest {
@Test
public void getMonster(){
/**
*为什么写的是beans.xml
* new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
* 默认解析的是类路径下的beans.xml文件
*/
ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
/**
* ioc的结构是什么样的?
*
*/
Object monster01 = ioc.getBean("monster01");
System.out.println(monster01);
System.out.println("运行时类型: "+monster01.getClass());
Monster monster02 = ioc.getBean("monster02", Monster.class);
System.out.println(monster02);
}
//验证类路径:/C:/ide/IdeaProjects/llp-spring/out/production/llp-spring/
@Test
public void classPath(){
String path = this.getClass().getResource("/").getPath();
System.out.println(path);
}
@Test
public void getBean(){
ApplicationContext ioc =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
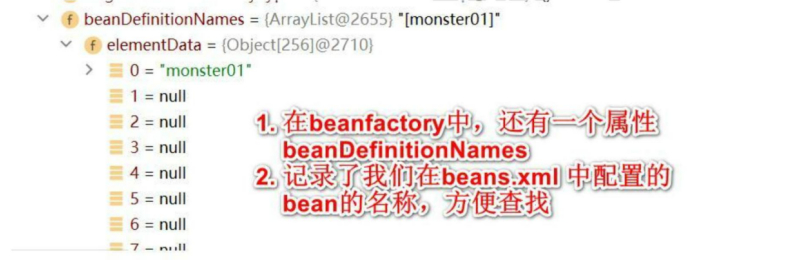
String[] beanIdArray = ioc.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String beanId : beanIdArray) {
System.out.println(beanId);
}
}
}
3.注意事项和细节
1.xml配置文件路径:默认解析的是类路径下的beans.xml文件,根据实际情况进行目录匹配
2.idea debug设置
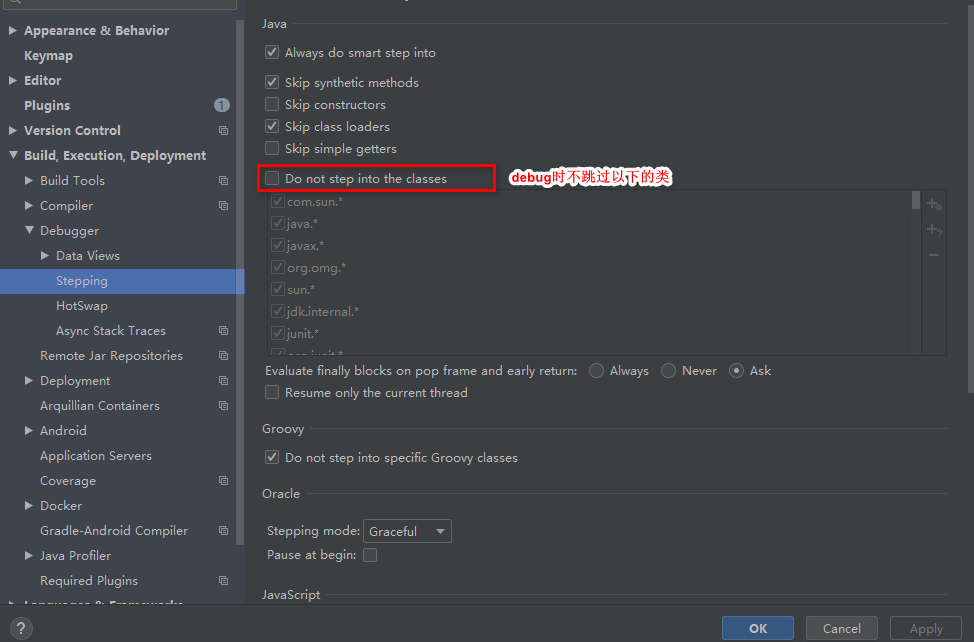

3.ioc容器的结构是什么样的
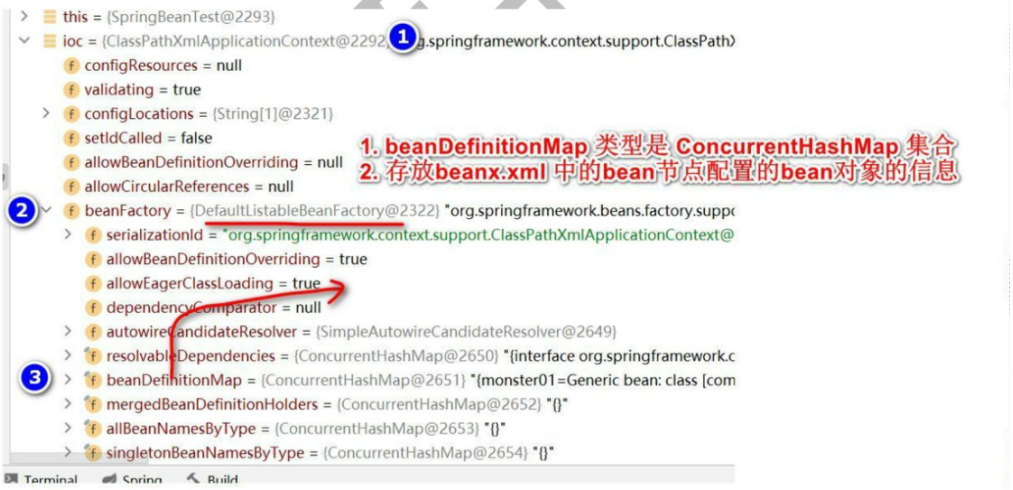
我们常说ioc是一个大的bean工厂
1.beanDefinitionMap属性,类型是ConcurrentHashMap集合
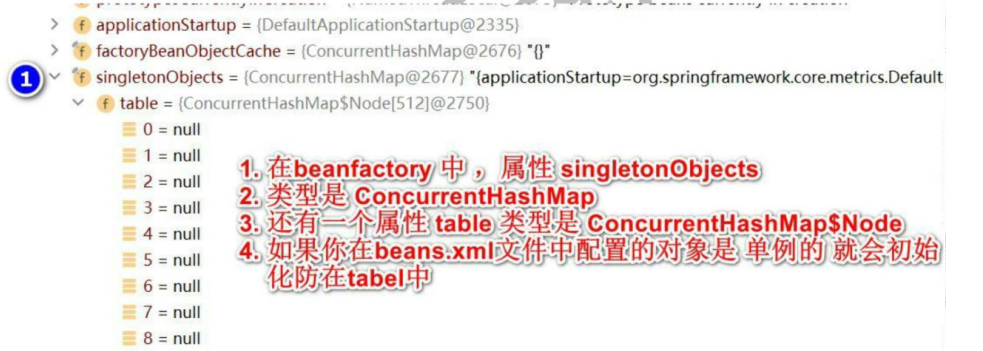
在beanDefinitionMap中有一个属性table,类型是ConcurrentHashMap$Node初始化长度为512,当超过时会进行扩容
数组每一个元素对应一个ConcurrentHashMap<k,V> key对应的是beanName 、value对应的时xml配置的Monster对象
2.在getBean(“monster01”)获取对象时,底层会从beanDefinitionMap中查找,看这个对象时不是配置的单列,如果时单列则从singletonObjects中获取对象,如果不是单列则创建一个monster对象进行返回



4、查看容器注入了哪些 bean 对象,会输出 bean 的 id
底层结构倒推API的使用
@Test
public void getBean(){
ApplicationContext ioc =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
String[] beanIdArray = ioc.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String beanId : beanIdArray) {
System.out.println(beanId);
}
}
4.图解

5.手动开发- 简单的 Spring 基于 XML 配置的程序
1.需求说明
- 自己写一个简单的 Spring 容器, 通过读取 beans.xml,获取第 1 个 JavaBean: Monster 的
对象,并给该的对象属性赋值,放入到容器中, 输出该对象信息.


2.思路分析
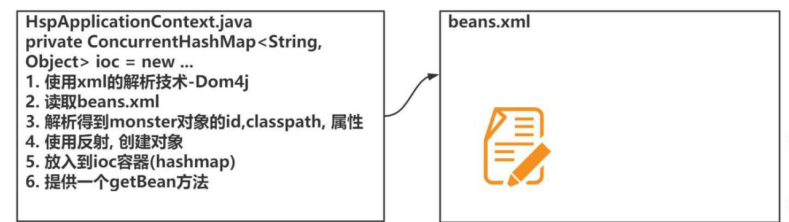
3.完成步骤
1.导入dom4j jar包
LlpApplicationContext-自定义容器
/**
* 1. 这个程序用于实现Spring的一个简单容器机制
* 2. 这里我们实现如何将beans.xml文件进行解析,并生成对象,放入容器中
* 3. 提供一个方法 getBean(id) 返回对应的对象
*/
public class LlpApplicationContext<T> {
private ConcurrentMap<String, Object> singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
//构造器
//接受一个容器的配置文件,比如beans.xml,该文件默认在src下
public LlpApplicationContext(String iocBeanXmlFile) throws Exception {
//1.得到类加载路径
//path = /C:/ide/IdeaProjects/llp-spring/out/production/llp-spring/
String path = this.getClass().getResource("/").getPath();
//2. 创建 Saxreader
SAXReader saxReader = new SAXReader();
//3. 得到Document对象
Document document = saxReader.read(path + iocBeanXmlFile);
//4. 得到rootDocument
Element rootElement = document.getRootElement();
/**
* 根标签换行
* <bean class="com.llp.spring.bean.Monster" id="monster01"> 0 1
* <property name="monsterId" value="1"/> 2
* <property name="name" value="孙悟空"/> 3
* <property name="skill" value="打妖怪"/> 4
* </bean>5 6
*/
//5. 得到第一个bean-monster01
List<Element> elements = rootElement.elements("bean");
Element bean = elements.get(0);
//获取xml标签中属性的值
String id = bean.attributeValue("id");
String fullClassPath = bean.attributeValue("class");
//6. 获取到第一个bean-monster01的相关属性
List<Element> property = bean.elements("property");
Element element = property.get(0);
String monsterId = element.attributeValue("value");
String name = property.get(1).attributeValue("value");
String skill = property.get(2).attributeValue("value");
//7.通过反射创建对象
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName(fullClassPath);
Object o = aClass.newInstance();
System.out.println("运行时类型:" + o.getClass());
//8.给对象赋值
Monster monster = (Monster) o;
monster.setMonsterId(Integer.parseInt(monsterId));
monster.setName(name);
monster.setSkill(skill);
// Method[] declaredMethods = aClass.getDeclaredMethods();
// for (Method declaredMethod : declaredMethods) {
// String methodName = declaredMethod.getName();
// declaredMethod.invoke()
// }
//9.将创建好的对象放到singletonObjects中
singletonObjects.put(id,monster);
}
/**
* 根据id获取bean
*
* @param id
* @return
*/
public Object getBean(String id) {
return singletonObjects.getOrDefault(id, null);
}
public T getBean(String id, Class<T> cls) {
return cls.cast(singletonObjects.getOrDefault(id, null));
}
}
LlpApplicationContextTest-测试类
public class LlpApplicationContextTest {
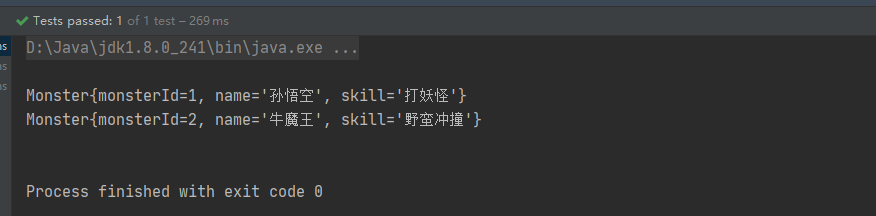
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
LlpApplicationContext llpApplicationContext = new LlpApplicationContext("beans.xml");
Object monster01 = llpApplicationContext.getBean("monster01");
System.out.println("monster01 = " + monster01);
Monster o = (Monster) monster01;
System.out.println(o.getMonsterId());
System.out.println(o.getName());
System.out.println(o.getSkill());
Monster monster = (Monster) llpApplicationContext.getBean("monster01", Monster.class);
System.out.println(monster);
}
}
beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--
1. 配置monster对象/javabean
2. 在beans中可以配置多个bean
3. bean表示就是一个java对象
4. class属性是用于指定类的全路径->spring底层使用反射创建
5. id属性表示该java对象在spring容器中的id, 通过id可以获取到对象
6. <property name="monsterId" value="100"> 用于给该对象的属性赋值
-->
<bean class="com.llp.spring.bean.Monster" id="monster01">
<property name="monsterId" value="1"/>
<property name="name" value="孙悟空"/>
<property name="skill" value="打妖怪"/>
</bean>
<bean class="com.llp.spring.bean.Monster" id="monster02">
<property name="monsterId" value="2"/>
<property name="name" value="牛魔王"/>
<property name="skill" value="野蛮冲撞"/>
</bean>
</beans>
6.思考题
- 在 beans.xml 中,我们注入 2 个 Monster 对象, 但是不指定 id,如下
<bean class="com.hspedu.spring.beans.Monster" >
<property name="monsterId" value="1010"/>
<property name="name" value="牛魔王~"/>
<property name="skill" value="芭蕉扇~"/>
</bean>
<bean class="com.hspedu.spring.beans.Monster">
<property name="monsterId" value="666"/>
<property name="name" value="牛魔王~~!!"/>
<property name="skill" value="芭蕉扇~~"/>
</bean>
问题 1:运行会不会报错
答: 不会报错,正常运行
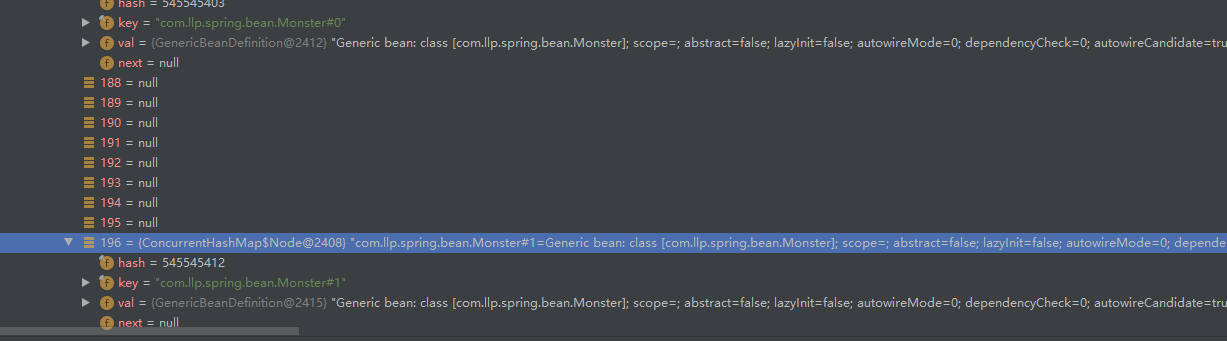
问题 2:如果不报错, 你能否找到分配的 id, 并获得到该对象.
答: 系统会默认分配 id ,分配 id 的规则是 全类名#0 , 全类名#1 这样的规则来分配 id, 我们可以通过 debug 方式来查看.
@Test
public void homeWork01(){
ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans02.xml");
Monster monster01 = (Monster) ioc.getBean("com.llp.spring.bean.Monster#0");
System.out.println(monster01);
Monster monster02 = (Monster) ioc.getBean("com.llp.spring.bean.Monster#1");
System.out.println(monster02);
}
Debug
测试结果
 JavaSE
JavaSE
 JavaWeb
JavaWeb
 Spring
Spring
 MyBatis
MyBatis
 linux
linux
 消息队列
消息队列
 工具
工具
 片段
片段
 AI
AI
 搜索
搜索