两种Controller层接口鉴权方式
两种Controller层接口鉴权方式
最近在做一个即时通讯服务时,要求对每个接口的入参进行鉴权处理,这里我整理出来了两种方式:1.基于注解和拦截器鉴权 2.基于注解和AOP鉴权
这里我在采用的是aop的方式,拦截器这里只完成了伪代码进行作为记录。
1.基于注解和拦截器鉴权
拦截器的方式主要需要解决requestBody重复获取的问题
1.首先我们需要定义一个鉴权标识的注解
/**
* 鉴权标记注解
*/
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Documented
public @interface Authorization {
}
2.重写HttpServletRequestWrapper
通过自定义的HttpServletRequestWrapper 备份一下流的数据,自定义HttpServletRequestWrapper 调用父类request.getInputStream()读取全部数据出来保存在一个byte数组内,当再次获取流数据的时候,自定义的HttpServletRequestWrapper 就会用byte数组重新生成一个新的流。备份的流数据仍然保留在byte数组中。
public class RepeatableReadRequestWrapper extends HttpServletRequestWrapper {
private final byte[] bytes;
public RepeatableReadRequestWrapper(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
super(request);
request.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
bytes = request.getReader().readLine().getBytes();
}
@Override
public BufferedReader getReader() throws IOException {
return new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(getInputStream()));
}
@Override
public ServletInputStream getInputStream() throws IOException {
ByteArrayInputStream bais = new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes);
return new ServletInputStream() {
@Override
public boolean isFinished() {
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean isReady() {
return false;
}
@Override
public void setReadListener(ReadListener readListener) {
}
@Override
public int read() throws IOException {
return bais.read();
}
@Override
public int available() throws IOException {
return bytes.length;
}
};
}
}
3.定义一个拦截器
@Component
public class RepeatSubmitInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Autowired
RedisCache redisCache;
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
if (handler instanceof HandlerMethod) {
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = (HandlerMethod) handler;
Method method = handlerMethod.getMethod();
if (method.isAnnotationPresent(Authorization.class)) {
//请求参数字符串
String nowParams = "";
if (request instanceof RepeatableReadRequestWrapper) {
try {
nowParams = ((RepeatableReadRequestWrapper) request).getReader().readLine();
System.out.println("nowParams: " + nowParams);
//TODO 进行鉴权处理
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
return true;
}
}
4.定义一个过滤器
public class RepeatableRequestFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) servletRequest;
if (StringUtils.startsWithIgnoreCase(request.getContentType(), "application/json")) {
RepeatableReadRequestWrapper requestWrapper = new RepeatableReadRequestWrapper(request, (HttpServletResponse) servletResponse);
filterChain.doFilter(requestWrapper,servletResponse);
return;
}
filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest, servletResponse);
}
}
5.配置类
@Configuration
public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Autowired
RepeatSubmitInterceptor repeatSubmitInterceptor;
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(repeatSubmitInterceptor).addPathPatterns("/**");
}
@Bean
FilterRegistrationBean<RepeatableRequestFilter> repeatableRequestFilterFilterRegistrationBean() {
FilterRegistrationBean<RepeatableRequestFilter> bean = new FilterRegistrationBean<>();
bean.setFilter(new RepeatableRequestFilter());
bean.addUrlPatterns("/*");
return bean;
}
}
6.测试类
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@Authorization
@PostMapping("/test")
public String authorization(@RequestBody User user) {
System.out.println(user);
return "succes";
}
}
测试结果
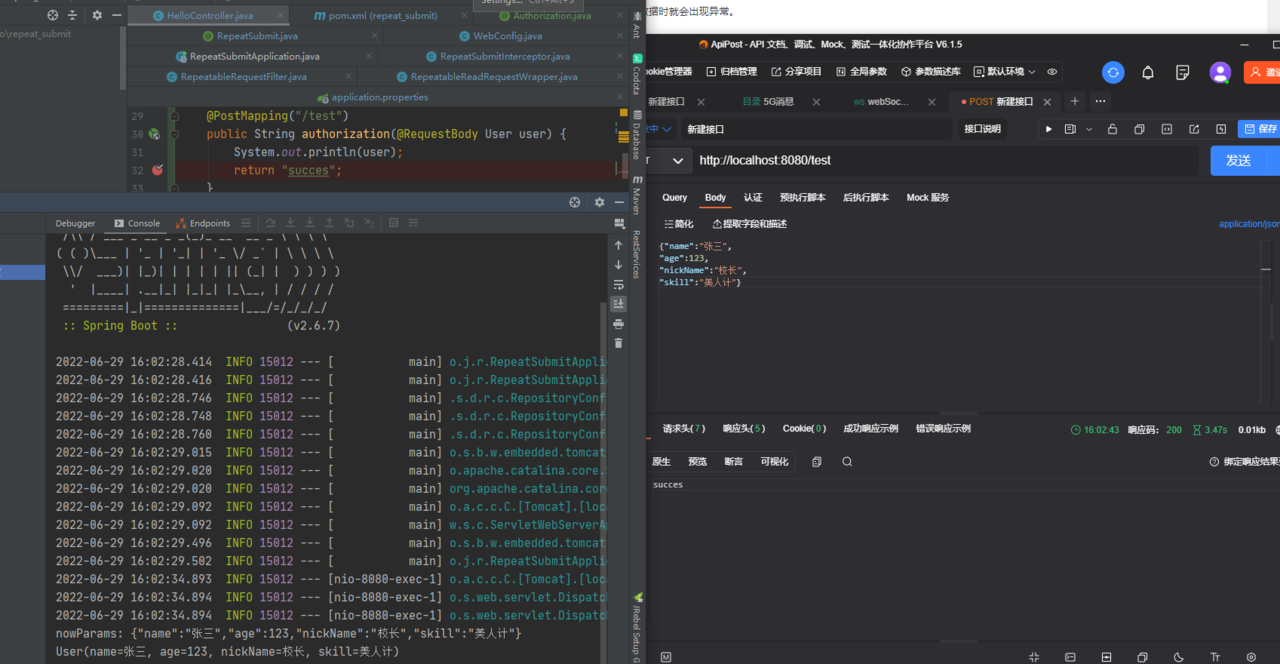
2.基于注解和AOP鉴权
1.定义一个鉴权标识注解
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Authorization {
}
2.定义AOP类
@Aspect
@Order(value = Integer.MAX_VALUE-1)
@Component
public class AuthorizationAspect {
private static Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AuthorizationAspect.class);
@Autowired
private AuthConfigService authConfigService;
@Before(value = "@annotation(com.llp.api.annotation.Authorization))")
public void authorization(JoinPoint joinPoint) throws Exception {
//获取请求参数
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
//获取方法签名
MethodSignature methodSignature = (MethodSignature) signature;
//获取Method对象
Method method = methodSignature.getMethod();
//判断方法是否被我们自定义的@Authorization注解修饰
if (method.isAnnotationPresent(Authorization.class)) {
//遍历请求参数
for (Object arg : args) {
//判断请求参数是否属于BaseConfigRequest类型
if (arg instanceof BaseConfigRequest) {
//属于,则对请求参数进行强转
BaseConfigRequest baseConfigRequest = (BaseConfigRequest) arg;
log.info("鉴权基类-baseConfigRequest:{}", ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(baseConfigRequest));
//获取鉴权id
String appId = baseConfigRequest.getAppId();
//获取密文
String cipherText = baseConfigRequest.getCipherText();
//通过鉴权id获取鉴权配置对象
EduAuthConfig authConfig = authConfigService.getAuthConfig(appId);
log.info("authConfig:{}", ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(authConfig));
//如果通过鉴权id没有查询到则抛出异常鉴权失败
Assert.notNull(authConfig, "未查询到appId对应的鉴权配置信息,鉴权失败");
//根据密文、私钥进行解密获取到鉴权key
String appKey = RSAUtil.decrypt(cipherText, authConfig.getPrivateKey());
log.info("解密后得到appKey:{}", appKey);
//如果鉴权key为空或者解密出来的鉴权key和配置的鉴权key不相同则抛出异常鉴权失败
if (appKey == null || !appKey.equals(authConfig.getAppKey())) {
throw new BaseException("鉴权参数错误,鉴权失败");
}
//鉴权通过结束循环
return;
}
}
}
}
}
3.定义一个鉴权基类
@Data
@ApiModel(value = "鉴权基类")
public class BaseConfigRequest<T> implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "鉴权Id")
@NotBlank(message = "鉴权id不能为空")
private String appId;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "密文")
@NotBlank(message = "密文不能为空")
private String cipherText;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "其他任意数据",notes = "在做鉴权时使用@Valid注解开启校验")
@Valid
private T data;
}
4.测试方法
@Authorization
@ApiOperation(value = "接收消息")
@RequestMapping(value = "/receiveMsg", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public BaseResult<String> receiveMsg(@Validated @RequestBody BaseConfigRequest<MessageSendRequest> request) {
return BaseResult.judgeOperate(messageService.receiveMsg(request));
}
 JavaSE
JavaSE
 JavaWeb
JavaWeb
 Spring
Spring
 MyBatis
MyBatis
 linux
linux
 消息队列
消息队列
 工具
工具
 片段
片段
 AI
AI
 搜索
搜索