MyBatis-缓存-提高检索效率的利器
MyBatis-缓存-提高检索效率的利器
1.缓存-官方文档
文档地址:https://mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/sqlmap-xml.html#cache
2.一级缓存
1.基本介绍
● 基本说明
- 默认情况下,mybatis 是启用一级缓存的/本地缓存/local Cache,它是 SqlSession 级别的。
- 同一个 SqlSession 接口对象调用了相同的 select 语句,会直接从缓存里面获取,而不是再去查询数据库
● 一级缓存原理图
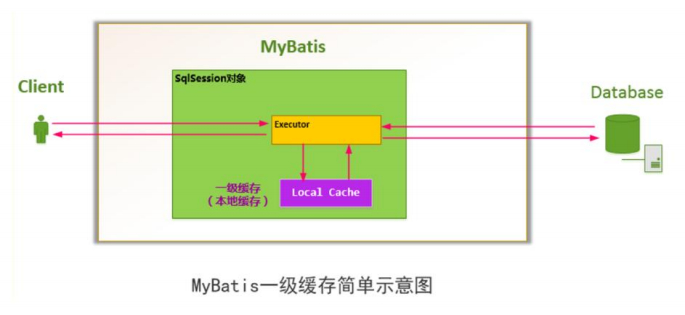
2.一级缓存
1.快速入门
需求: 当我们第 1 次查询 id=1 的 Monster 后,再次查询 id=1 的 monster 对象,就会直接 从一级缓存获取,不会再次发出 sql
-
创建新module: mybatis_cache , 必要的文件和配置直接从mybatis_quickstart module 拷贝即可
-
需要拷贝的文件和配置如图
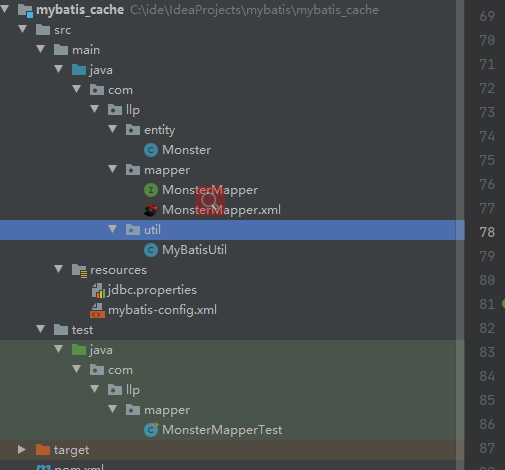
-
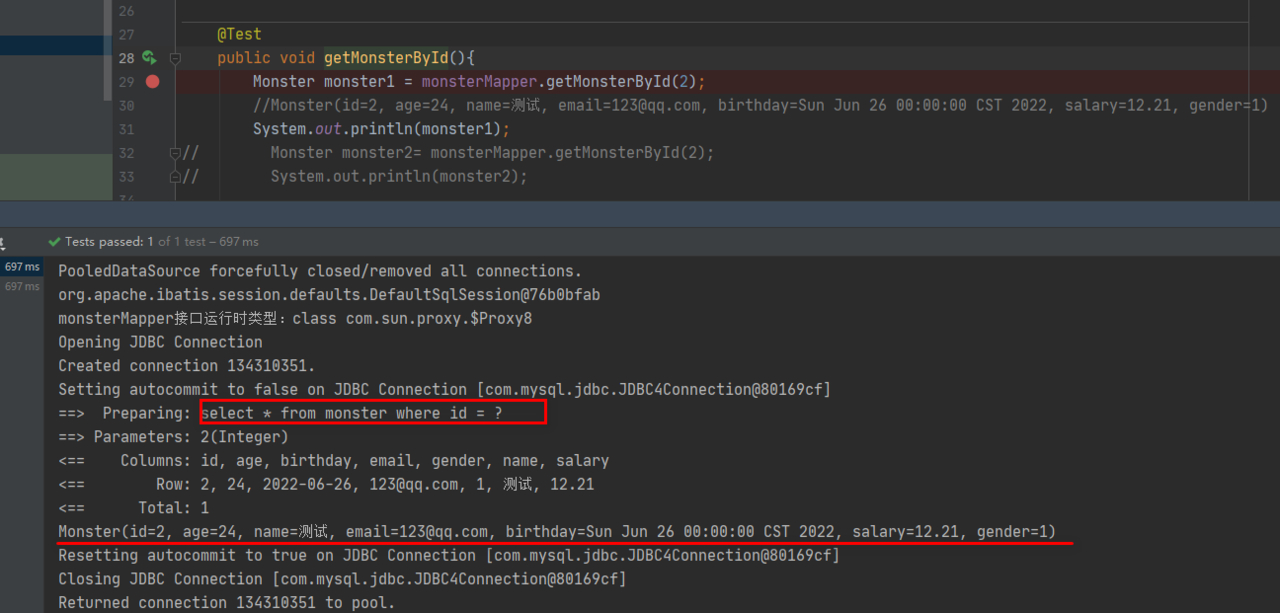
使用 MonsterMapperTest.java , 运行 getMonsterById() 看看是否可以看到日志输出, 结论我们多次运行,总是会发出 SQL.
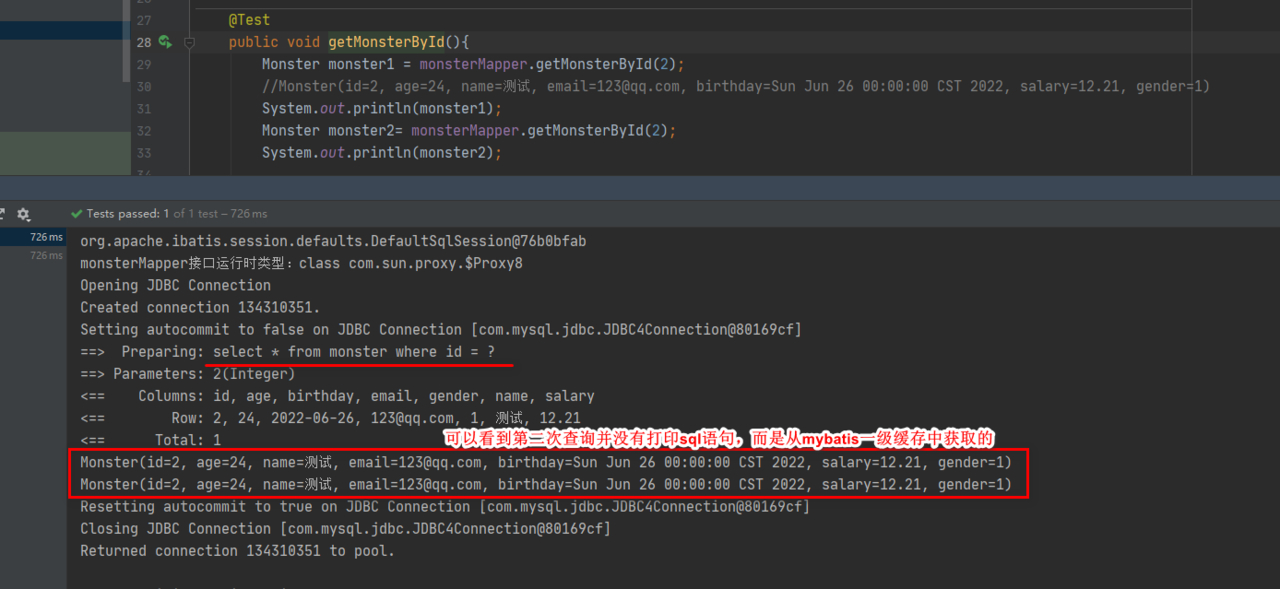
4. 修改MonsterMapperTest.java, 增加测试方法, 测试一级缓存的基本使用
2.Debug一级缓存执行流程
1.一级缓存中没有数据执行流程
Monster monster1 = monsterMapper.getMonsterById(2); monsterMapper是一个接口,MyBatis而真正的实现时MapperProxy.java这个动态代理类去执行目标方法
MapperProxy.java
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else {
//proxy:代理类
//method:目标方法
//args:方法参数
//sqlSession:DefaultSqlSession
return cachedInvoker(method).invoke(proxy, method, args, sqlSession);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
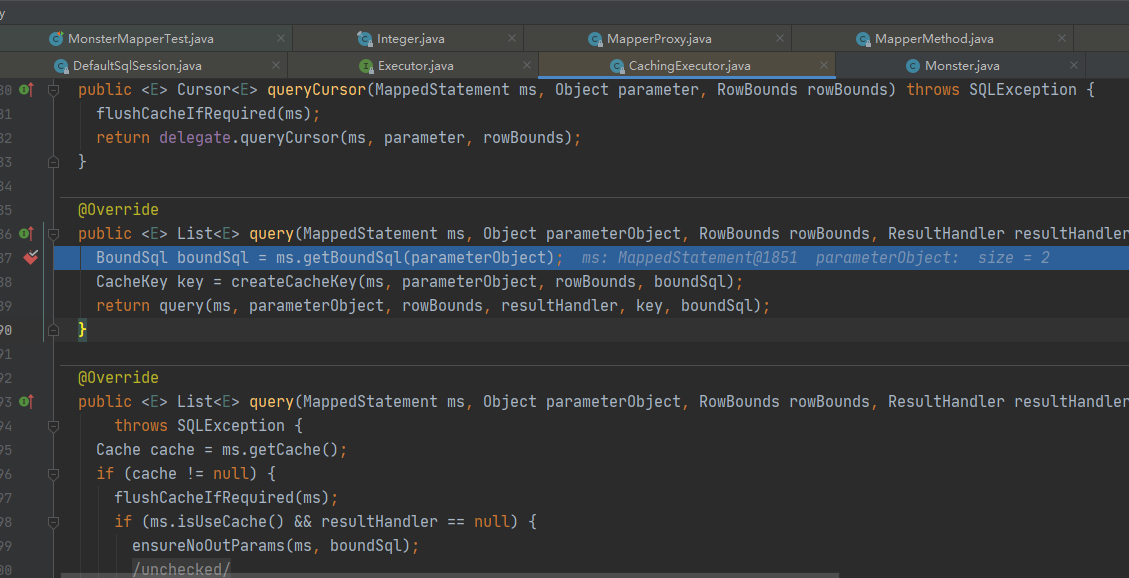
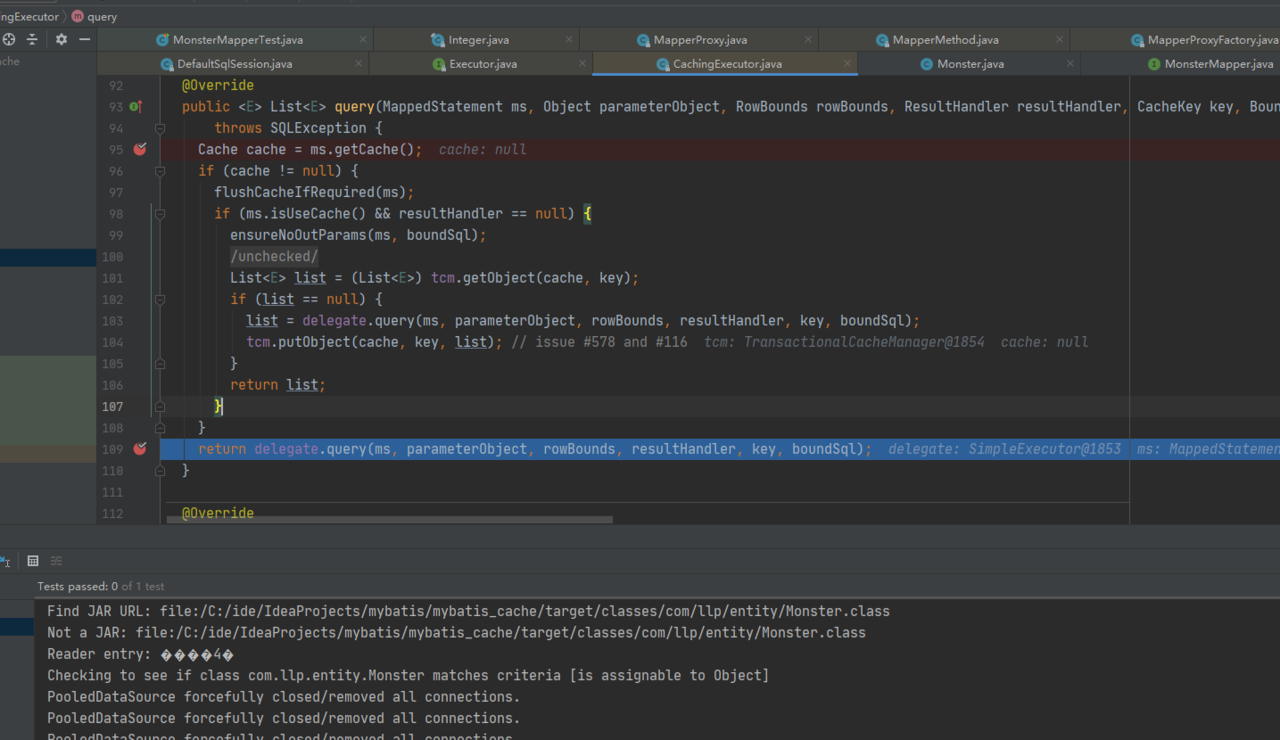
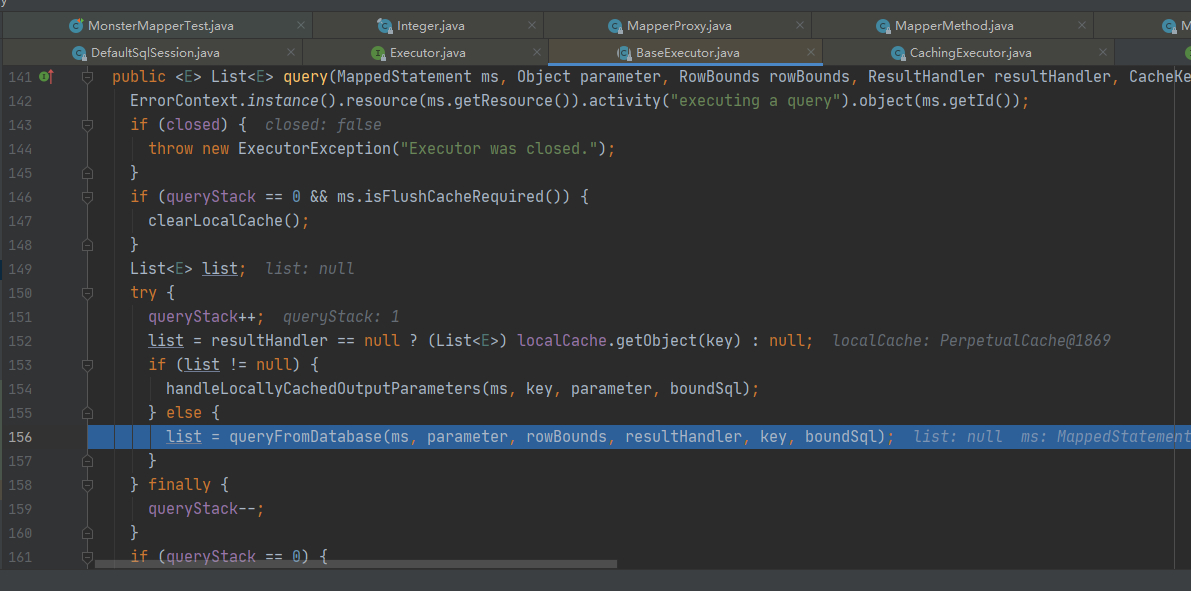
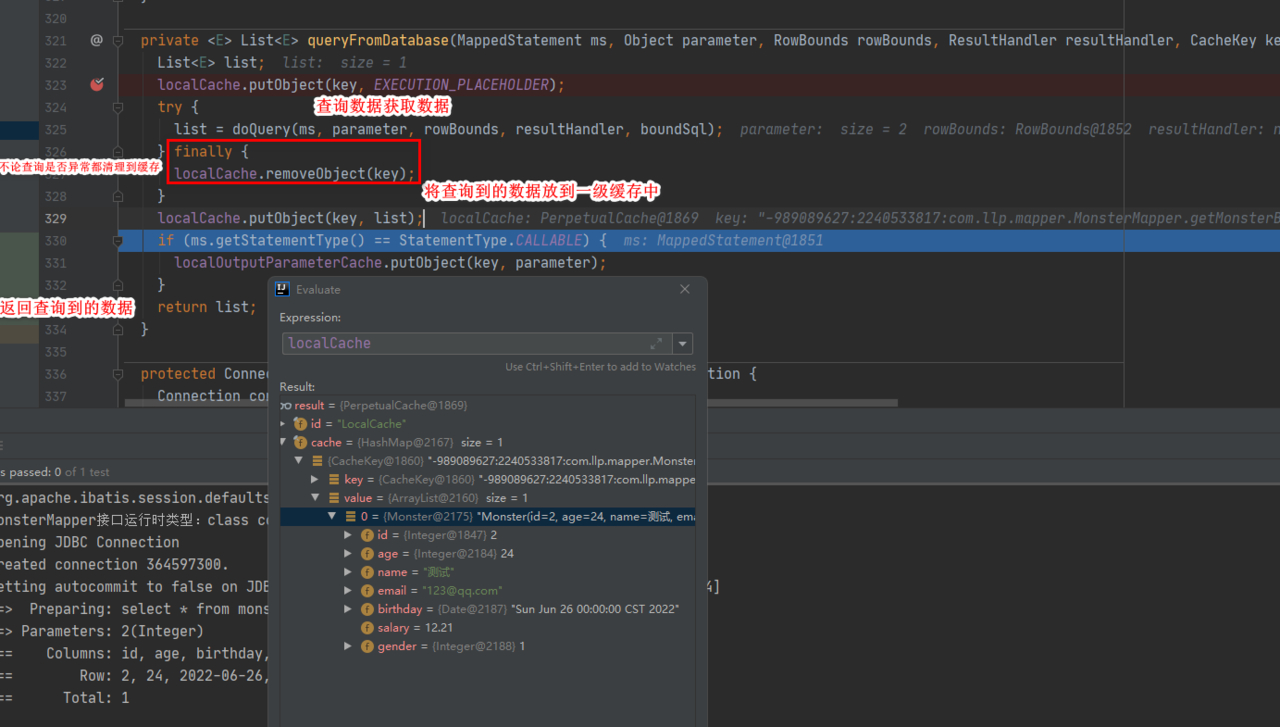
2.一级缓存中获取数据执行流程
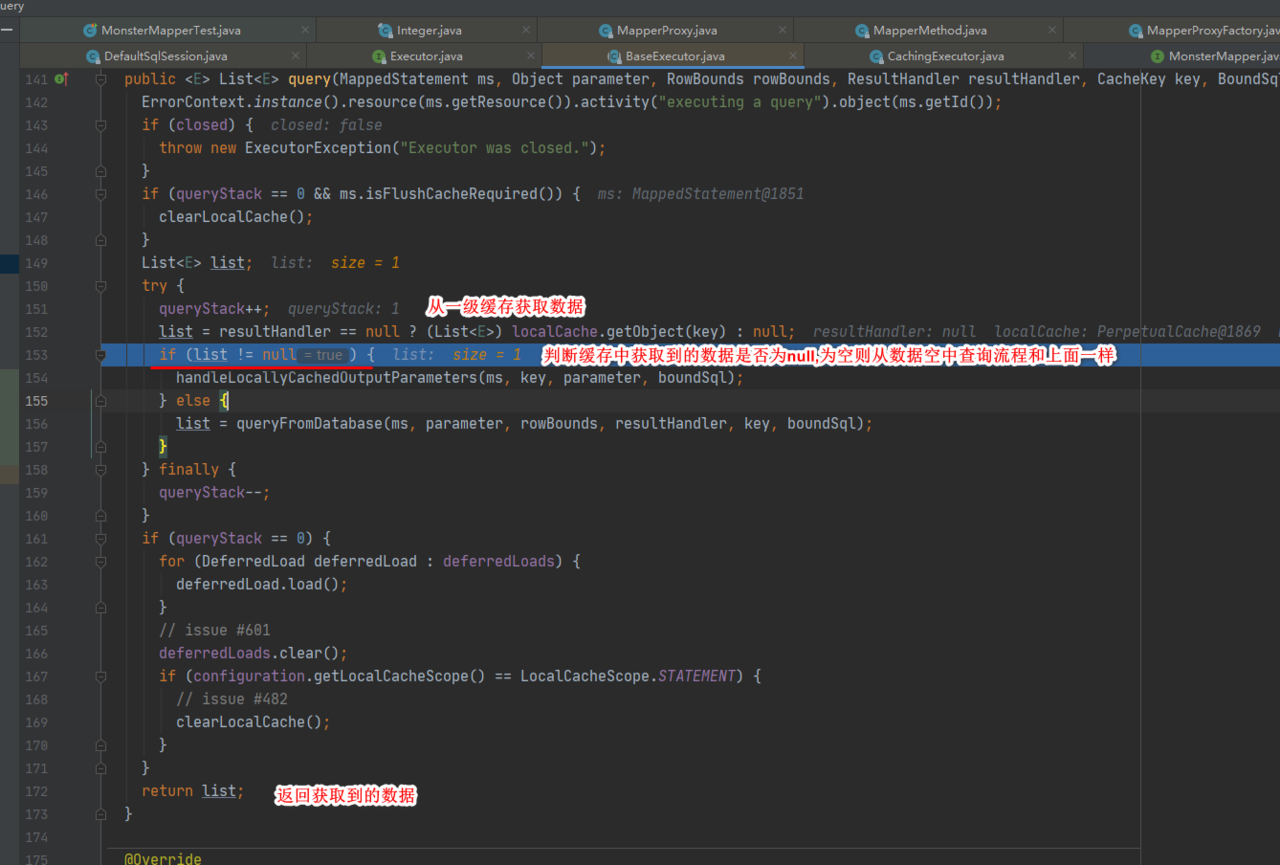
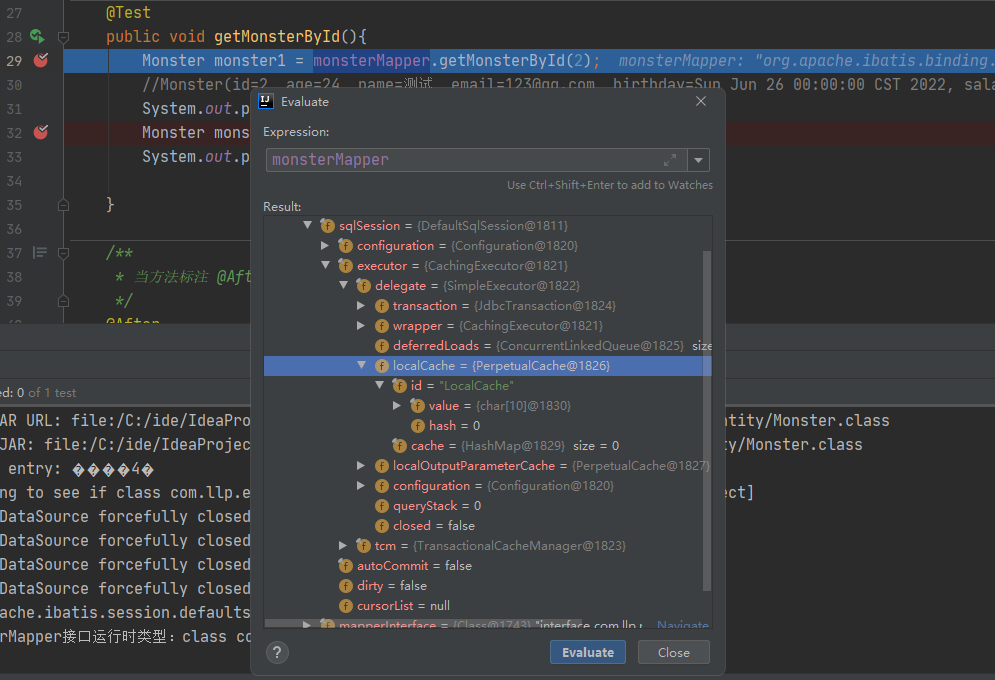
3.一级缓存失效分析
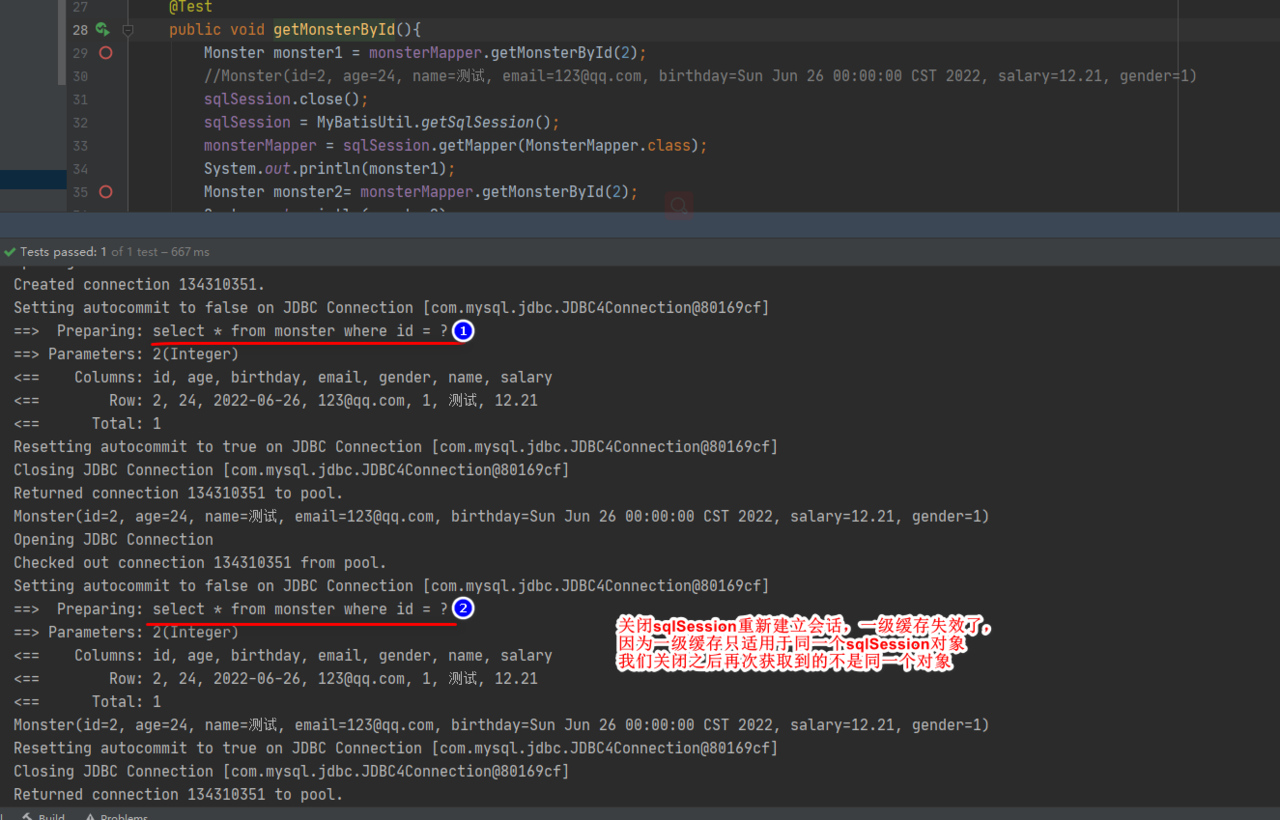
- 关闭 sqlSession 会话后, 再次查询,会到数据库查询, 修改 MonsterMapperTest.java, 测试一级缓存失效情况
@Test
public void getMonsterById(){
Monster monster1 = monsterMapper.getMonsterById(2);
//Monster(id=2, age=24, name=测试, email=123@qq.com, birthday=Sun Jun 26 00:00:00 CST 2022, salary=12.21, gender=1)
sqlSession.close();
sqlSession = MyBatisUtil.getSqlSession();
monsterMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(MonsterMapper.class);
System.out.println(monster1);
Monster monster2= monsterMapper.getMonsterById(2);
System.out.println(monster2);
}
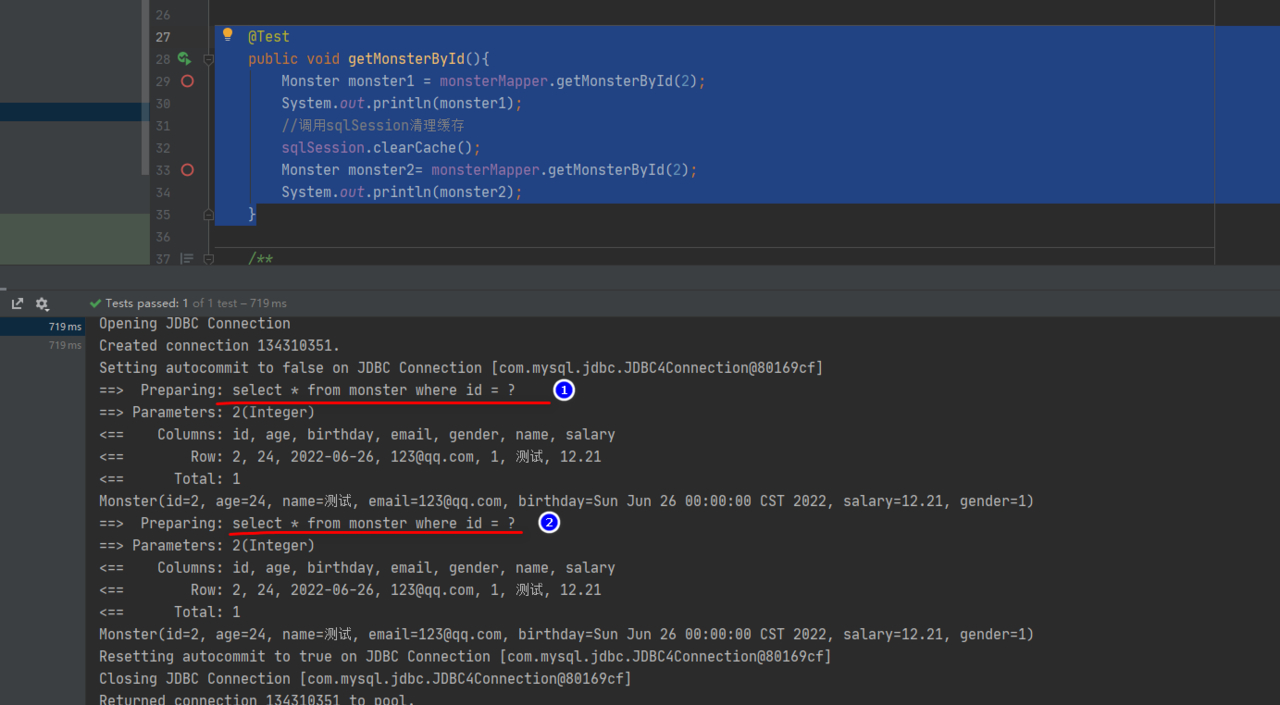
2. 当执行 sqlSession.clearCache() 会使一级缓存失效,修改 MonsterMapperTest.java, 测 试一级缓存失效情况
@Test
public void getMonsterById(){
Monster monster1 = monsterMapper.getMonsterById(2);
System.out.println(monster1);
//sqlSession清理缓存
sqlSession.clearCache();
Monster monster2= monsterMapper.getMonsterById(2);
System.out.println(monster2);
}
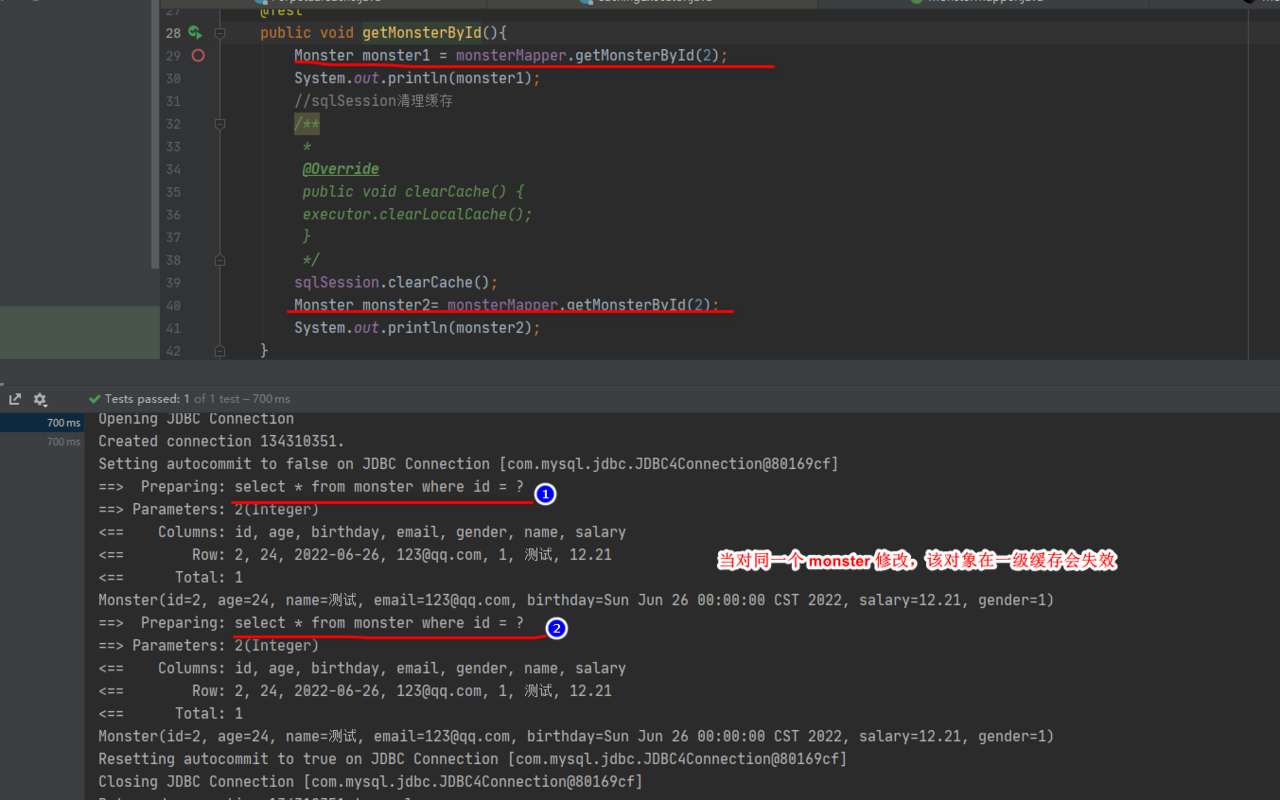
- 当对同一个 monster 修改,该对象在一级缓存会失效, 修改 MonsterMapperTest.java, 测 试一把
@Test
public void getMonsterById(){
Monster monster1 = monsterMapper.getMonsterById(2);
System.out.println(monster1);
//sqlSession清理缓存
/**
*
@Override
public void clearCache() {
executor.clearLocalCache();
}
*/
sqlSession.clearCache();
Monster monster2= monsterMapper.getMonsterById(2);
System.out.println(monster2);
}
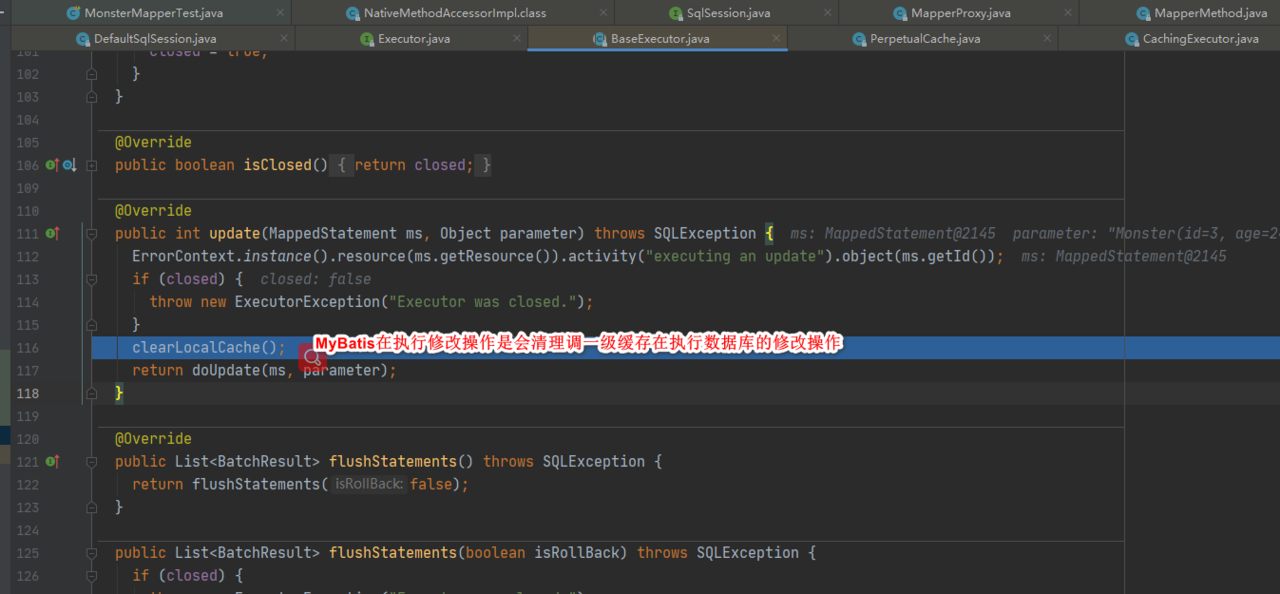
@Override
public void clearLocalCache() {
if (!closed) {
localCache.clear();
localOutputParameterCache.clear();
}
}
3.二级缓存
1.基本介绍
● 基本介绍
- 二级缓存和一级缓存都是为了提高检索效率的技术
- 最大的区别就是作用域的范围不一样,一级缓存的作用域是 sqlSession 会话级别,在一次 会话有效,而二级缓存作用域是全局范围,针对不同的会话都有效
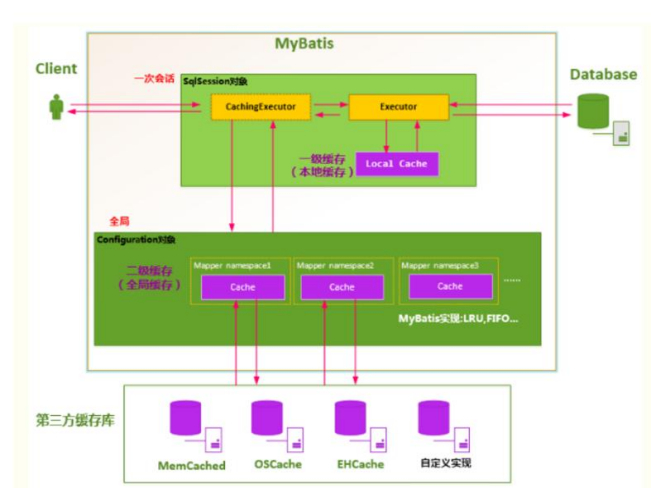
● 二级缓存原理图
2.二级缓存快速入门
- mybatis-config.xml 配置中开启二级缓存
MyBatis默认是开启二级缓存的,cacheEnabled默认为true
<!--
mybatis默认开启二级缓存
1、全局性地开启或关闭所有映射器配置文件中已配置的任何缓存, 可以理解这是一个总开关
2、默认就是: true
-->
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
- 使用二级缓存时 entity 类实现序列化接口 (serializable),因为二级缓存可能使用到序列化(比如EHCache可能从磁盘、内存获取数据,而从磁盘去获取数据的时候就需要用到反序列化)技术
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Data
public class Monster implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
//属性-和表字段有对应关系
private Integer id;
private Integer age;
private String name;
private String email;
private Date birthday;
private double salary;
private Integer gender;
}
- 在对应的 XxxMapper.xml 中设置二级缓存的策略

<!--
1、配置二级缓存: 是mybatis自带
2、FIFO – 先进先出:按对象进入缓存的顺序来移除它们。
3. flushInterval 刷新间隔 是毫秒单位 60000 表示 60s
4. size="512": 引用数目, 属性可以被设置为任意正整数, 默认1024
5. readOnly="true": (只读)属性可以被设置为 true 或 false: 如果我们只是用于读操作,
建议设置成 true, 这样可以提示效率, 如果有修改操作,设置成 false, 默认就是false
注意事项:
1.mybatis默认是开启二级缓存的,不过需要让其生效还需在对应的mapper中进行配置
2.mybatis一级缓存是基于sqlsession为生命周期的
3.mybatis的二级缓存是基于application为生命周期的,以namesapce为单位
4.当在不同的namesapce对表进行增删改操作时需要注意缓存生效的namespace,
如果不是在配置开启二级缓存的namespace下进行,那么不会更新二级缓存会导致数据脏读
-->
<cache eviction="FIFO" flushInterval="60000"
size="512" readOnly="true"/>
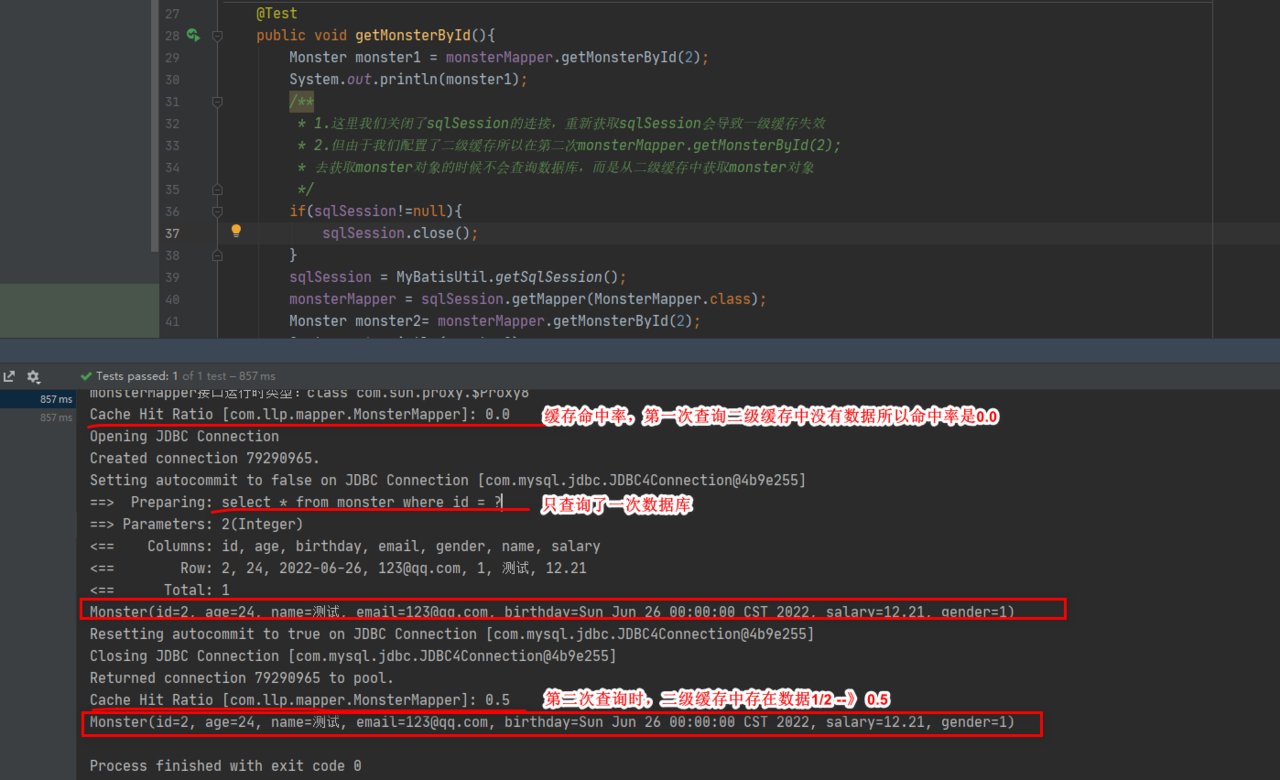
- 修改 MonsterMapperTest.java , 完成测试
@Test
public void getMonsterById(){
Monster monster1 = monsterMapper.getMonsterById(2);
System.out.println(monster1);
/**
* 1.这里我们关闭了sqlSession的连接,重新获取sqlSession会导致一级缓存失效
* 2.但由于我们配置了二级缓存所以在第二次monsterMapper.getMonsterById(2);
* 去获取monster对象的时候不会查询数据库,而是从二级缓存中获取monster对象
*/
if(sqlSession!=null){
sqlSession.close();
}
sqlSession = MyBatisUtil.getSqlSession();
monsterMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(MonsterMapper.class);
Monster monster2= monsterMapper.getMonsterById(2);
System.out.println(monster2);
}
3.Debug二级缓存执行流程
1.第一次查询二级缓存中没有数据时查询执行流程
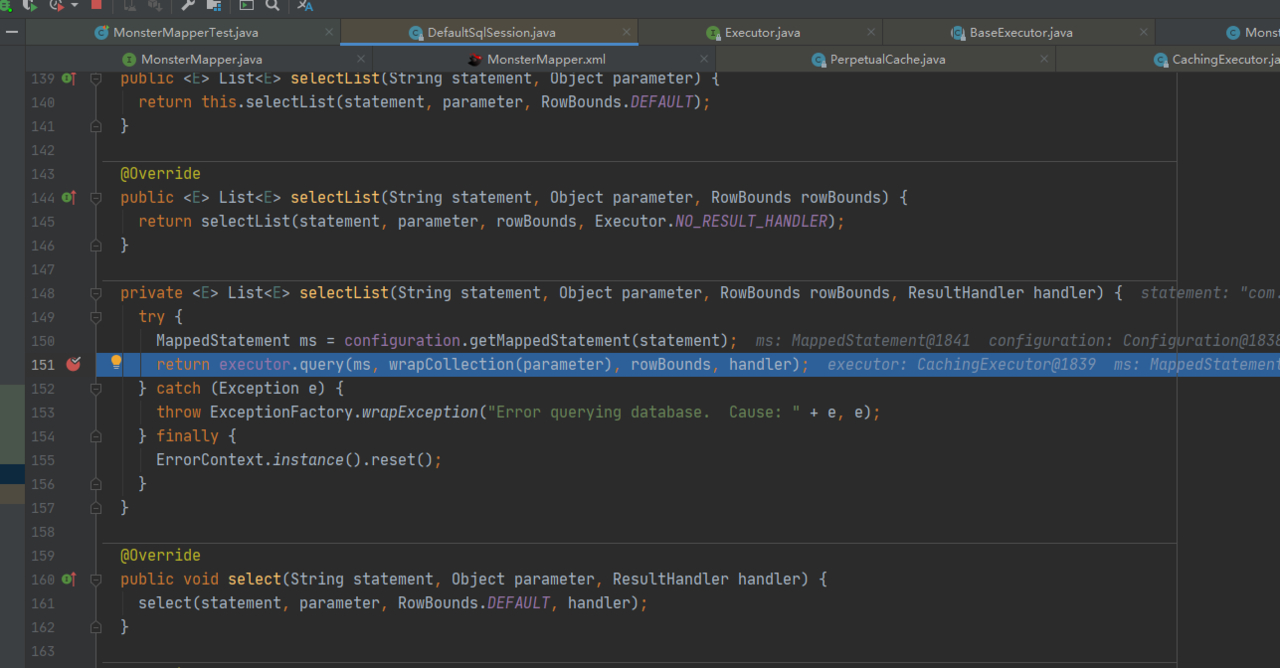
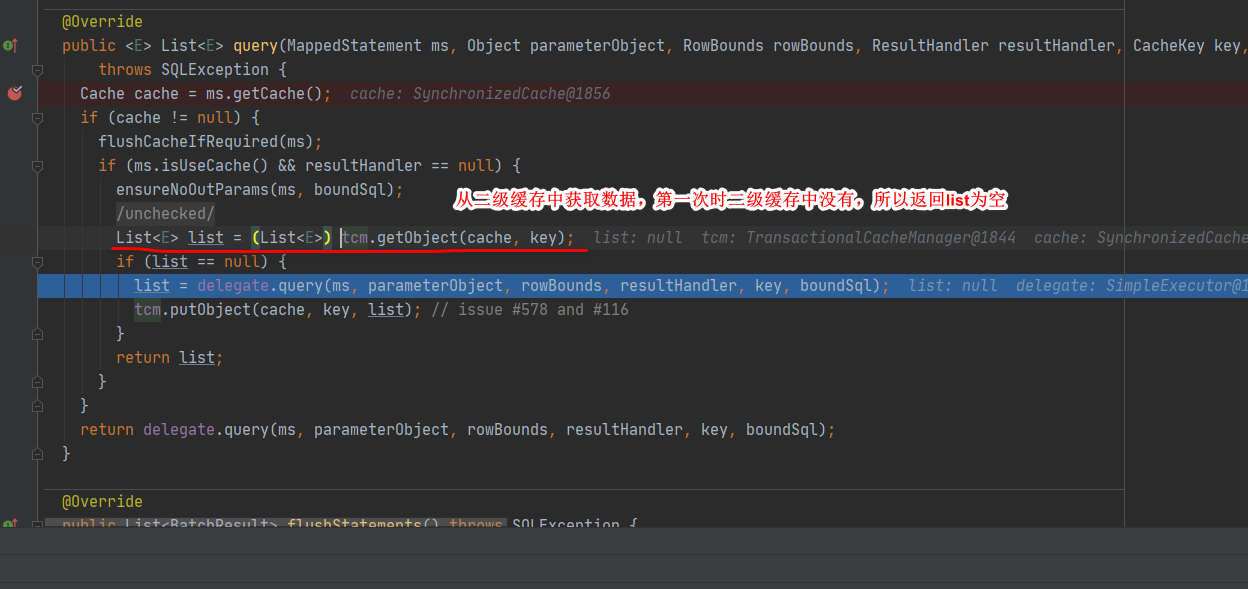

2.二级缓存中存在数据时查询执行流程
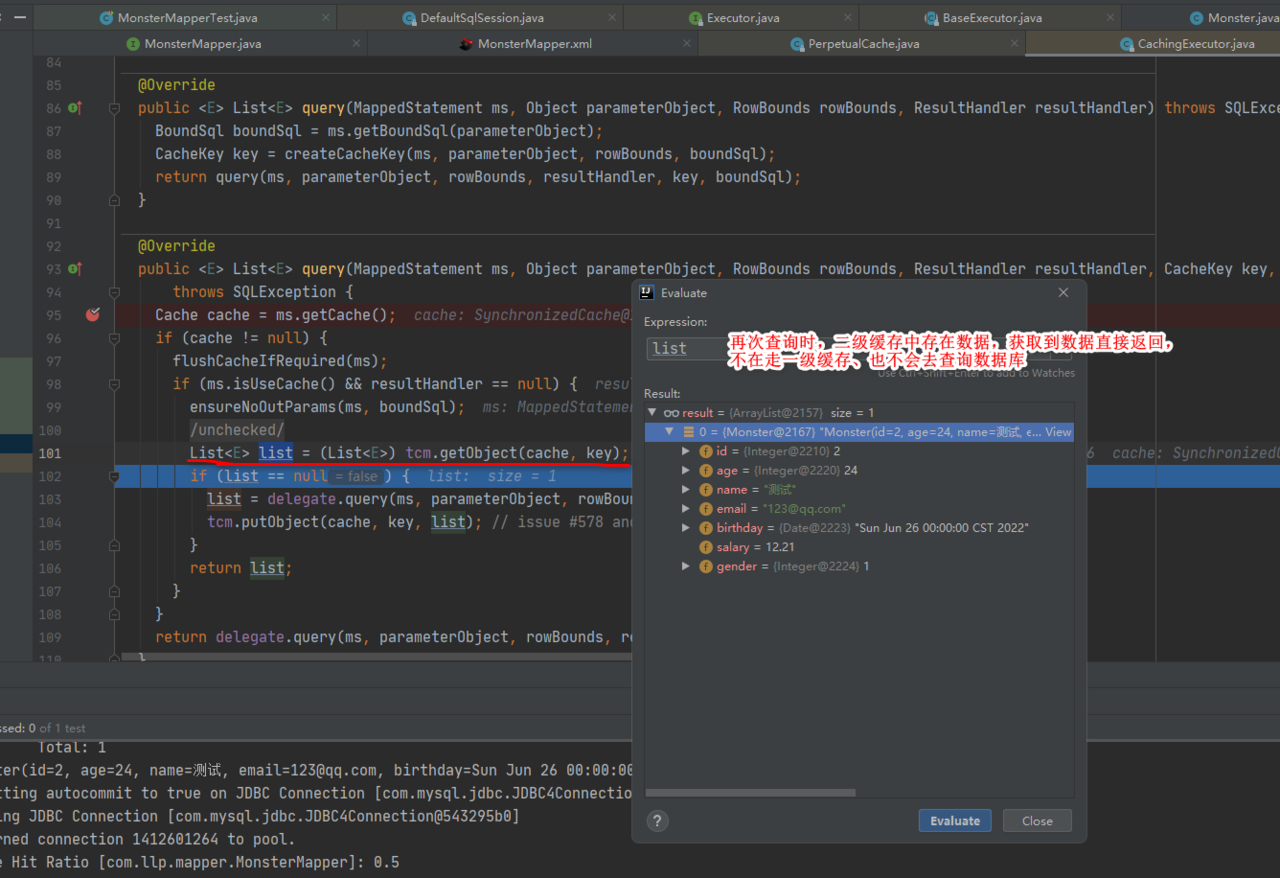
4.注意事项和使用细节
具体参数配置参考官网:https://mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/sqlmap-xml.html#cache
1.理解二级缓存策略的参数
<!-- FIFO: 创建了 FIFO 的策略,每隔 30 秒刷新一次,最多存放 360 个对象而且返回的对象被认为是 只读的 -->
<cache eviction="FIFO" flushInterval="30000" size="360" readOnly="true"/>
上面的配置意思如下:
eviction:缓存的回收策略
默认的清除策略是 LRU。可用的清除策略有:
LRU – 最近最少使用:移除最长时间不被使用的对象。
FIFO – 先进先出:按对象进入缓存的顺序来移除它们。
SOFT – 软引用:基于垃圾回收器状态和软引用规则移除对象。
WEAK – 弱引用:更积极地基于垃圾收集器状态和弱引用规则移除对象。
flushInterval:时间间隔,单位是毫秒, 默认情况是不设置,也就是没有刷新间隔,缓存仅仅会在调用语句时刷新。
size:引用数目,内存大就多配置点,要记住你缓存的对象数目和你运行环境的可用内存 资源数目。默认值是 1024
readOnly: (1)true,只读的缓存会给所有调用者返回缓存对象的相同实例。 因此这些对象不能被修改。
(2)fase可读写,可读写的缓存会(通过序列化)返回缓存对象的拷贝。 速度上会慢一些,但是更安全,因此默认值是 false。
2.四大策略
√ LRU – 最近最少使用的:移除最长时间不被使用的对象,它是默认
√ FIFO – 先进先出:按对象进入缓存的顺序来移除它们。
√ SOFT – 软引用:移除基于垃圾回收器状态和软引用规则的对象。
√ WEAK – 弱引用:更积极地移除基于垃圾收集器状态和弱引用规则的对象。
3. 如何禁用二级缓存
1.全局性的禁用二级缓存
<settings>
<!--全局性地开启或关闭所有映射器配置文件中已配置的任何缓存, 默认就是 true-->
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="false"/>
</settings>
2.在xxxMapper.xml中,如果我们没有添加类型<cache eviction="FIFO" flushInterval="30000" size="360" readOnly="true"/>这样的配置,二级缓存时不会生效的,mybatis的二级缓存是基于application为生命周期的,以namesapce为单位
<!--<cache eviction="FIFO" flushInterval="30000" size="360" readOnly="true"/>-->
3.更加细粒度的, 在配置方法上指定
<!--
useCache="false"
1.设置 useCache=false 可以禁用当前 select 语句的二级缓存,即每次查询都会发出 sql 去查询
2.默认情况是 true,即该 sql 使用二级缓存
-->
<select id="getMonsterById" resultType="com.llp.entity.Monster" useCache="false">
select * from monster where id = #{id}
</select>
4. mybatis 刷新二级缓存的设置
<update id="updateMonster" parameterType="Monster" flushCache="true">
UPDATE mybatis_monster SET NAME=#{name},age=#{age} WHERE id=#{id}
</update>
insert、update、delete 操作数据后需要刷新缓存,如果不执行刷新缓存会出现脏读, flushCache默认为 true,默认情况下为 true 即刷新缓存,一般不用修改。
5.细节补充
1.mybatis默认是开启二级缓存的,不过需要让其生效还需在对应的mapper中进行配置
2.mybatis一级缓存是基于sqlsession为生命周期的
3.mybatis的二级缓存是基于application为生命周期的,以namesapce为单位
4.当在不同的namesapce对表进行增删改操作时需要注意缓存生效的namespace,如果不是在配置开启二级缓存的namespace下进行,那么不会更新二级缓存会导致数据脏读
4.Mybatis 的一级缓存和二级缓存执行顺序
1.执行顺序
缓存执行顺序是:二级缓存-->一级缓存-->数据库
2.小实验
//演示二级缓存->一级缓存->DB执行的顺序
@Test
public void cacheSeqTest() {
System.out.println("查询第1次");
//DB, 会发出SQL, 分析cache hit ratio 0.0
Monster monster1 = monsterMapper.getMonsterById(3);
System.out.println(monster1);
//这里关闭sqlSession, 一级缓存数据没有
//当我们关闭一级缓存的时候,如果你配置二级缓存,那么一级缓存的数据,会放入到二级缓存
sqlSession.close();
sqlSession = MyBatisUtil.getSqlSession();
monsterMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(MonsterMapper.class);
System.out.println("查询第2次");
//从二级缓存获取id=3 monster , 就不会发出SQL, 分析cache hit ratio 0.5
Monster monster2 = monsterMapper.getMonsterById(3);
System.out.println(monster2);
System.out.println("查询第3次");
//从二级缓存获取id=3 monster, 不会发出SQL, 分析cache hit ratio 0.6666
Monster monster3 = monsterMapper.getMonsterById(3);
System.out.println(monster3);
if (sqlSession != null) {
sqlSession.close();
}
System.out.println("操作成功");
}
3.细节说明
- 不会出现一级缓存和二级缓存中有同一个数据。因为二级缓存(数据)是在一级缓存关闭 之后才有的
5.EhCache 缓存
1.配置文档
https://www.cnblogs.com/zqyanywn/p/10861103.html
2.基本介绍
-
EhCache 是一个纯 Java 的缓存框架,具有快速、精干等特点
-
MyBatis 有自己默认的二级缓存(前面我们已经使用过了),但是在实际项目中,往往使用 的是更加专业的第三方缓存产品 作为 MyBatis 的二级缓存,EhCache 就是非常优秀的缓存 产品
- MyBatis 默认情况(即一级缓存)是使用的 PerpetualCache 类实现 Cache 接口的,是核心类
-
当我们使用了 Ehcahce 后,就是 EhcacheCache 类实现 Cache 接口的,是核心类
3.配置和使用EhCache
- 加入相关依赖
<!--引入ehcache核心库/jar-->
<dependency>
<groupId>net.sf.ehcache</groupId>
<artifactId>ehcache-core</artifactId>
<version>2.6.11</version>
</dependency>
<!--引入需要使用的slf4j-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
<version>1.7.25</version>
</dependency>
<!--引入mybatis整合ehcache库/jar-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.caches</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-ehcache</artifactId>
<version>1.2.1</version>
</dependency>
- mybatis-config.xml 仍然打开二级缓存
<settings> <!-- 开启二级缓存,默认就是打开 --> <setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/> </settings> - 加 入\src\main\resources\ehcache.xml 配 置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ehcache>
<!--
diskStore:为缓存路径,ehcache分为内存和磁盘两级,此属性定义磁盘的缓存位置。参数解释如下:
user.home – 用户主目录
user.dir – 用户当前工作目录
java.io.tmpdir – 默认临时文件路径
-->
<diskStore path="java.io.tmpdir/Tmp_EhCache"/>
<!--
defaultCache:默认缓存策略,当ehcache找不到定义的缓存时,则使用这个缓存策略。只能定义一个。
-->
<!--
name:缓存名称。
maxElementsInMemory:缓存最大数目
maxElementsOnDisk:硬盘最大缓存个数。
eternal:对象是否永久有效,一但设置了,timeout将不起作用。
overflowToDisk:是否保存到磁盘,当系统宕机时
timeToIdleSeconds:设置对象在失效前的允许闲置时间(单位:秒)。仅当eternal=false对象不是永久有效时使用,可选属性,默认值是0,也就是可闲置时间无穷大。
timeToLiveSeconds:设置对象在失效前允许存活时间(单位:秒)。最大时间介于创建时间和失效时间之间。仅当eternal=false对象不是永久有效时使用,默认是0.,也就是对象存活时间无穷大。
diskPersistent:是否缓存虚拟机重启期数据 Whether the disk store persists between restarts of the Virtual Machine. The default value is false.
diskSpoolBufferSizeMB:这个参数设置DiskStore(磁盘缓存)的缓存区大小。默认是30MB。每个Cache都应该有自己的一个缓冲区。
diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds:磁盘失效线程运行时间间隔,默认是120秒。
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy:当达到maxElementsInMemory限制时,Ehcache将会根据指定的策略去清理内存。默认策略是LRU(最近最少使用)。你可以设置为FIFO(先进先出)或是LFU(较少使用)。
clearOnFlush:内存数量最大时是否清除。
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy:可选策略(清除策略)有:LRU(最近最少使用,默认策略)、FIFO(先进先出)、LFU(最少访问次数)。
FIFO,first in first out,这个是大家最熟的,先进先出。
LFU, Less Frequently Used,就是上面例子中使用的策略,直白一点就是讲一直以来最少被使用的。如上面所讲,缓存的元素有一个hit属性,hit值最小的将会被清出缓存。
LRU,Least Recently Used,最近最少使用的,缓存的元素有一个时间戳,当缓存容量满了,而又需要腾出地方来缓存新的元素的时候,那么现有缓存元素中时间戳离当前时间最远的元素将被清出缓存。
-->
<defaultCache
eternal="false"
maxElementsInMemory="10000"
overflowToDisk="false"
diskPersistent="false"
timeToIdleSeconds="1800"
timeToLiveSeconds="259200"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU"/>
</ehcache>
文档说明: https://www.taobye.com/f/view-11-23.html
4. 在 XxxMapper.xml 中启用 EhCache , 当然原来 MyBatis 自带的缓存配置就注销了
<!--配置/启用ehcache-->
<cache type="org.mybatis.caches.ehcache.EhcacheCache"/>
5. 修改 MonsterMapperTest.java , 增加测试方法, 完成测试+简单 Debug
//测试ehCache级缓存
@Test
public void ehCacheTest() {
//查询id=3的monster
Monster monster = monsterMapper.getMonsterById(3);
//会发出SQL, 到db查询
System.out.println("monster=" + monster);
//这里老师关闭sqlSession, 一级缓存[数据]失效.=> 将数据放入到二级缓存 (ehcache)
if (sqlSession != null) {
sqlSession.close();
}
//重新获取sqlSession
sqlSession = MyBatisUtils.getSqlSession();
//重新获取了monsterMapper
monsterMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(MonsterMapper.class);
//再次查询id=3的monster
System.out.println("--虽然前面关闭了sqlSession,因为配置二级缓存(ehcache), " +
"当你再次查询相同的id时, 不会再发出sql, 而是从二级缓存(ehcache)获取数据----");
Monster monster2 = monsterMapper.getMonsterById(3);
System.out.println("monster2=" + monster2);
//再次查询id=3的monster, 仍然到二级缓存(ehcache), 获取数据, 不会发出sql
Monster monster3 = monsterMapper.getMonsterById(3);
System.out.println("monster3=" + monster3);
if (sqlSession != null) {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
执行机制和之前基本是一样的,只是缓存的实现方式不同
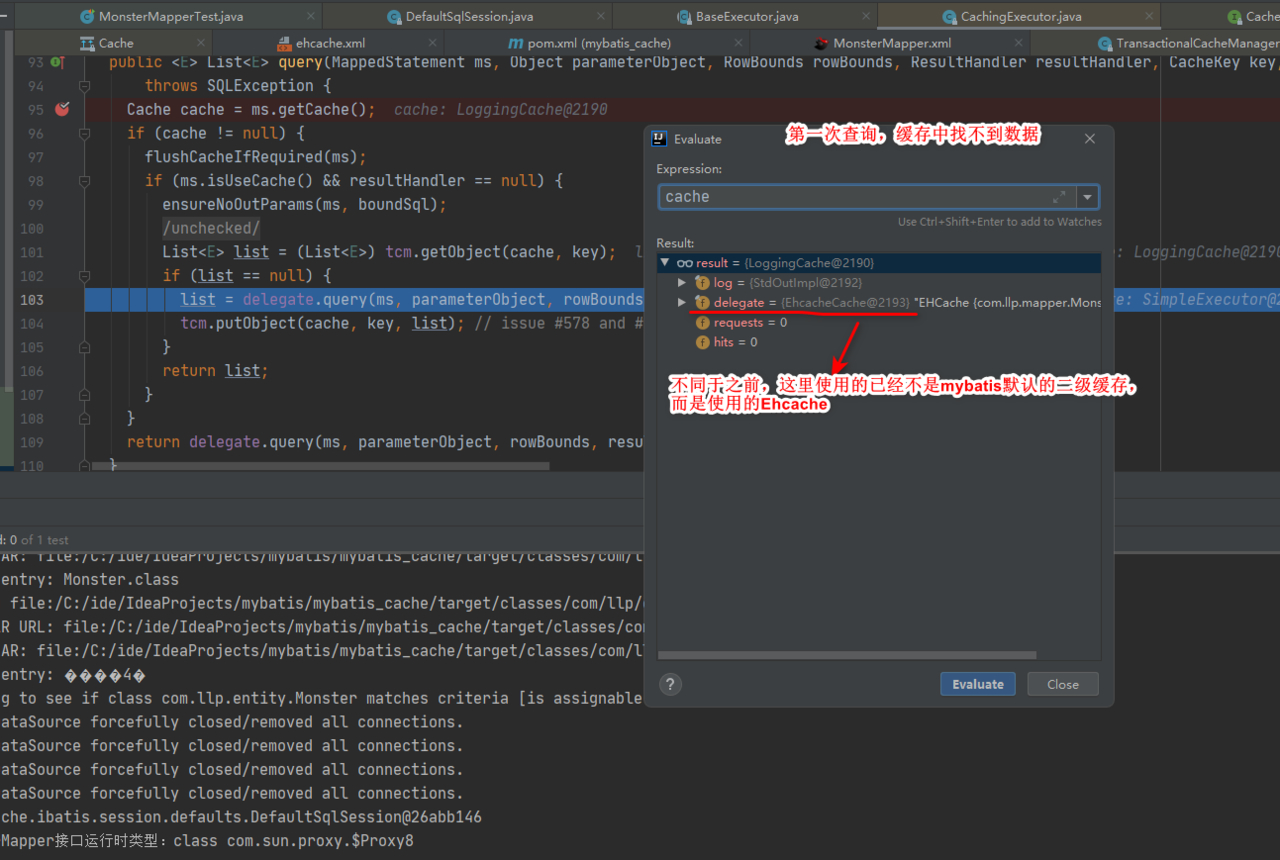
4.EhCache缓存细节说明
如何理解 EhCache 和 MyBatis 缓存的关系
- MyBatis 提供了一个接口 Cache【如图,找到 org.apache.ibatis.cache.Cache ,关联源 码包就可以看到 Cache 接口】
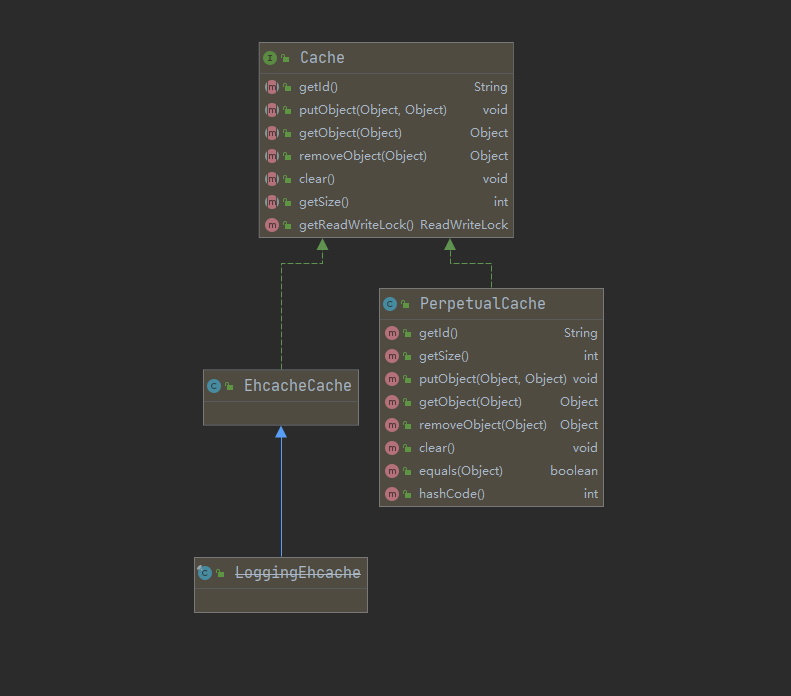
- 只要实现了该 Cache 接口,就可以作为二级缓存产品和 MyBatis 整合使用,Ehcache 就 是实现了该接口
- MyBatis 默认情况(即一级缓存)是使用的 PerpetualCache 类实现 Cache 接口的,是核心类

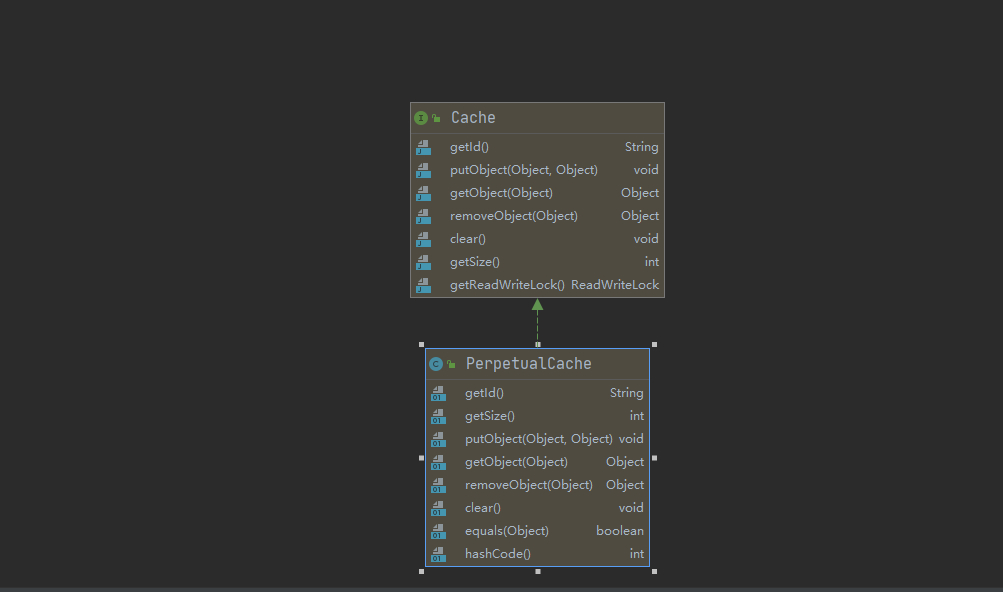
- 当我们使用了 Ehcahce 后,就是 EhcacheCache 类实现 Cache 接口的,是核心类.
 JavaSE
JavaSE
 JavaWeb
JavaWeb
 Spring
Spring
 MyBatis
MyBatis
 linux
linux
 消息队列
消息队列
 工具
工具
 片段
片段
 AI
AI
 搜索
搜索