SpringBoot整合JSR-303表单校验
SpringBoot整合JSR-303表单校验
思考一个问题,引出JSR-303
为什么前端做了参数校验,后端还要进行参数校验?
普通用户通过页面操作,前端可以校验住参数的正确性。但如果有人获取到接口,利用接口调用工具比如:postman对后端接口直接发起请求,这样就可以绕过前端校验,此时如果后端不做参数校验就不能保证数据规则。而JSR-303验证框架提供了丰富的参数校验注解来支持后端的表单校验。
1.概述
● 概述
- 对输入的数据(比如表单数据),进行必要的验证,并给出相应的提示信息。
- 对于验证表单数据,springMVC 提供了很多实用的注解, 这些注解由 JSR 303 验证框架提供
● JSR 303 验证框架
1.JSR 303 是 Java 为 Bean 数据合法性校验提供的标准框架,它已经包含在 JavaEE 中
-
JSR 303 通过在 Bean 属性上标注类似于 @NotNull、@Max 等标准的注解指定校验规则, 并通过标准的验证接口对 Bean 进行验证
-
JSR 303 提供的基本验证注解有:
空检查 @Null 验证对象是否为null @NotNull 验证对象是否不为null, 无法查检长度为0的字符串 @NotBlank 检查约束字符串是不是Null还有被Trim的长度是否大于0,只对字符串,且会去掉前后空格. @NotEmpty 检查约束元素是否为NULL或者是EMPTY. Booelan检查 @AssertTrue 验证 Boolean 对象是否为 true @AssertFalse 验证 Boolean 对象是否为 false 长度检查 @Size(min=, max=) 验证对象(Array,Collection,Map,String)长度是否在给定的范围之内 @Length(min=, max=) Validates that the annotated string is between min and max included. 日期检查 @Past 验证 Date 和 Calendar 对象是否在当前时间之前,验证成立的话被注释的元素一定是一个过去的日期 @Future 验证 Date 和 Calendar 对象是否在当前时间之后 ,验证成立的话被注释的元素一定是一个将来的日期 @Pattern 验证 String 对象是否符合正则表达式的规则,被注释的元素符合制定的正则表达式,regexp:正则表达式 flags: 指定 Pattern.Flag 的数组,表示正则表达式的相关选项。 数值检查 建议使用在Stirng,Integer类型,不建议使用在int类型上,因为表单值为“”时无法转换为int,但可以转换为Stirng为”“,Integer为null @Min 验证 Number 和 String 对象是否大等于指定的值 @Max 验证 Number 和 String 对象是否小等于指定的值 @DecimalMax 被标注的值必须不大于约束中指定的最大值. 这个约束的参数是一个通过BigDecimal定义的最大值的字符串表示.小数存在精度 @DecimalMin 被标注的值必须不小于约束中指定的最小值. 这个约束的参数是一个通过BigDecimal定义的最小值的字符串表示.小数存在精度 @Digits 验证 Number 和 String 的构成是否合法 @Digits(integer=,fraction=) 验证字符串是否是符合指定格式的数字,interger指定整数精度,fraction指定小数精度。 @Range(min=, max=) 被指定的元素必须在合适的范围内 @Range(min=10000,max=50000,message=”range.bean.wage”) @Valid 递归的对关联对象进行校验, 如果关联对象是个集合或者数组,那么对其中的元素进行递归校验,如果是一个map,则对其中的值部分进行校验.(是否进行递归验证) @CreditCardNumber信用卡验证 @Email 验证是否是邮件地址,如果为null,不进行验证,算通过验证。 @ScriptAssert(lang= ,script=, alias=) //验证URL是否正确 @URL(protocol=,host=, port=,regexp=, flags=)
● Hibernate Validator 扩展注解
- Hibernate Validator 和 Hibernate 没有关系,只是 JSR 303 实现的一个扩展.
- Hibernate Validator 是 JSR 303 的一个参考实现,除支持所有标准的校验注解外,它还支 持以下的扩展注解:
- 扩展注解有如下

2.应用实例
1.基础校验
准备工作
1.创建SpringBoot项目
2.引入依赖,以SpringBoot为例,spring-boot-starter-web依赖中包含了校验框架。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
代码实现
1.controller层代码,使用@Validated开启校验
@RestController
@RequestMapping("commodity/brand")
public class BrandController {
@Autowired
private BrandService brandService;
/**
* 信息
*/
@RequestMapping("/info/{id}")
public R info(@PathVariable("id") Long id) {
BrandEntity brand = brandService.getById(id);
return R.ok().put("brand", brand);
}
/**
* 保存
* @Validated({SaveGroup.class})
* 指定分组校验之后,@Validated修饰的类,每个字段必须指定组否则校验不会生效
*/
@RequestMapping("/save")
public R save(@Validated @RequestBody BrandEntity brand) {
brandService.save(brand);
return R.ok();
}
/**
* 修改
*/
@RequestMapping("/update")
public R update(@Validated @RequestBody BrandEntity brand) {
brandService.updateById(brand);
return R.ok();
}
}
说明:开启校验需要在方法入参使用@Validated修饰
@Valid与@Validated区别:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_33274797/article/details/109060226
2.在@Validated修饰的类上,不同类型字段上添加对应的验证注解
@Data
@TableName("commodity_brand")
public class BrandEntity implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@TableId
@Null(message = "添加不能指定id")
private Long id;
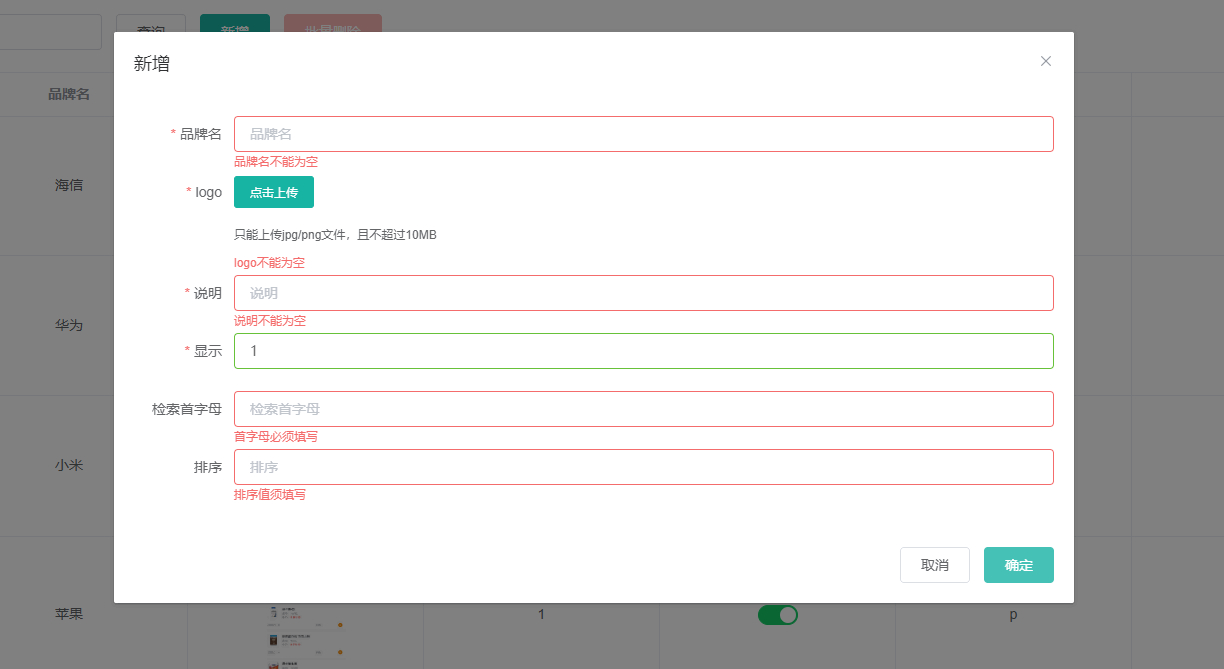
@NotBlank(message = "品牌名不能为空")
private String name;
/**
* logo
*/
@NotBlank(message = "logo不能为空")
@URL(message = "logo不是一个合法的URL")
private String logo;
/**
* 说明
*/
private String description;
/**
* 显示
*/
@NotNull(message = "显示状态不能为空")
private Integer isshow;
/**
* 检索首字母
*/
@NotBlank(message = "检索首字母不能为空")
@Pattern(regexp = "^[a-zA-Z]$", message = "检索字母必须是一个字母")
private String firstLetter;
/**
* 排序
*/
@NotNull(message = "排序值不能为空")
@Min(value = 0, message = "排序值要求大于等于 0")
private Integer sort;
}
测试
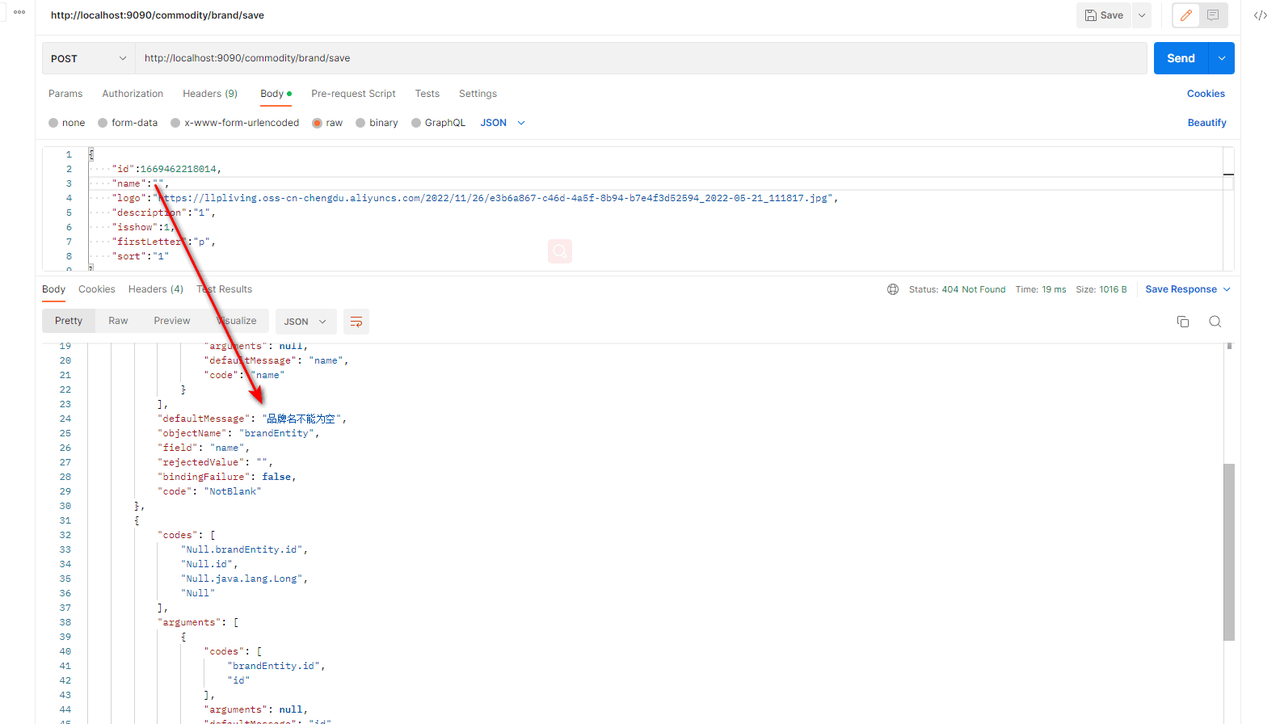
2.分组校验
为了满足新增、修改不同的参数校验,JSR-303校验框架还支持分组校验。这里以新增、修改为例
1.创建新增、修改分组校验标识接口
/**
* 没有什么具体代码,就在做一个分组的标识
* 表示新增组的校验标识
*/
public interface SaveGroup {
}
//用于修改组的校验标识
public interface UpdateGroup {
}
2.在controller层代码中修改@Validated注解,使用@Validated({分组类名.class})来进行分组校验
/**
* 保存
* @Validated({SaveGroup.class})
* 指定分组校验之后,@Validated修饰的类,每个字段必须指定组否则校验不会生效
*/
@RequestMapping("/save")
public R save(@Validated({SaveGroup.class}) @RequestBody BrandEntity brand) {
brandService.save(brand);
return R.ok();
}
/**
* 修改
*/
@RequestMapping("/update")
public R update(@Validated({UpdateGroup.class}) @RequestBody BrandEntity brand) {
brandService.updateById(brand);
return R.ok();
}
注意:@Validated注解指定分组校验之后,@Validated修饰的类,每个字段必须指定组否则校验不会生效
3.在@Validated修饰的类上,不同类型字段上添加对应的验证注解并标识不同的分组
@Data
@TableName("commodity_brand")
public class BrandEntity implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
/**
* id
* 1. @NotNull(message = "修改要求指定id",groups = {UpdateGroup.class})
* 表示@NotNull 在UpdateGroup校验组生效
* <p>
* 2. @Null(message = "添加不能指定id",groups = {SaveGroup.class})
* 表示@Null 在SaveGroup校验组生效
*/
@TableId
@NotNull(message = "修改要求id不能为空",groups ={UpdateGroup.class})
@Null(message = "添加不能指定id",groups = {SaveGroup.class})
private Long id;
/**
* 品牌名
* 说明
* 1. @NotBlank 表示name必须包括一个非空字符
* 2. message = "品牌名不能为空" 是老师指定的一个校验消息
* 3. 如果没有指定 message = "品牌名不能为空" ,就会返回默认的校验消息 key = javax.validation.constraints.NotBlank.message
* 4. 这个默认的消息是在 ValidationMessages_zh_CN.properties 文件配置 javax.validation.constraints.NotBlank.message = \u4e0d\u80fd\u4e3a\u7a7a
* 5. @NotBlank 可以用于 CharSequence
* 6. groups = {SaveGroup.class, UpdateGroup.class}
* 就是@NotBlank 在 SaveGroup 和 UpdateGroup都生效
*/
@NotBlank(message = "品牌名不能为空", groups = {SaveGroup.class, UpdateGroup.class})
private String name;
/**
* logo
*/
@NotBlank(message = "logo不能为空",groups = {SaveGroup.class, UpdateGroup.class})
@URL(message = "logo不是一个合法的URL",groups = {SaveGroup.class, UpdateGroup.class})
private String logo;
/**
* 说明
*/
private String description;
/**
* 显示
*/
@NotNull(message = "显示状态不能为空",groups = {SaveGroup.class, UpdateGroup.class})
private Integer isshow;
/**
* 检索首字母
*/
@NotBlank(message = "检索首字母不能为空",groups = {SaveGroup.class, UpdateGroup.class})
@Pattern(regexp = "^[a-zA-Z]$", message = "检索字母必须是一个字母",groups = {SaveGroup.class, UpdateGroup.class})
private String firstLetter;
/**
* 排序
*/
@NotNull(message = "排序值不能为空",groups = {SaveGroup.class, UpdateGroup.class})
@Min(value = 0, message = "排序值要求大于等于 0",groups = {SaveGroup.class, UpdateGroup.class})
private Integer sort;
}
说明,上面的代码表示添加时不需要填写id,修改时需要填写id; 其他参数修改、新增都做相同校验
4.测试
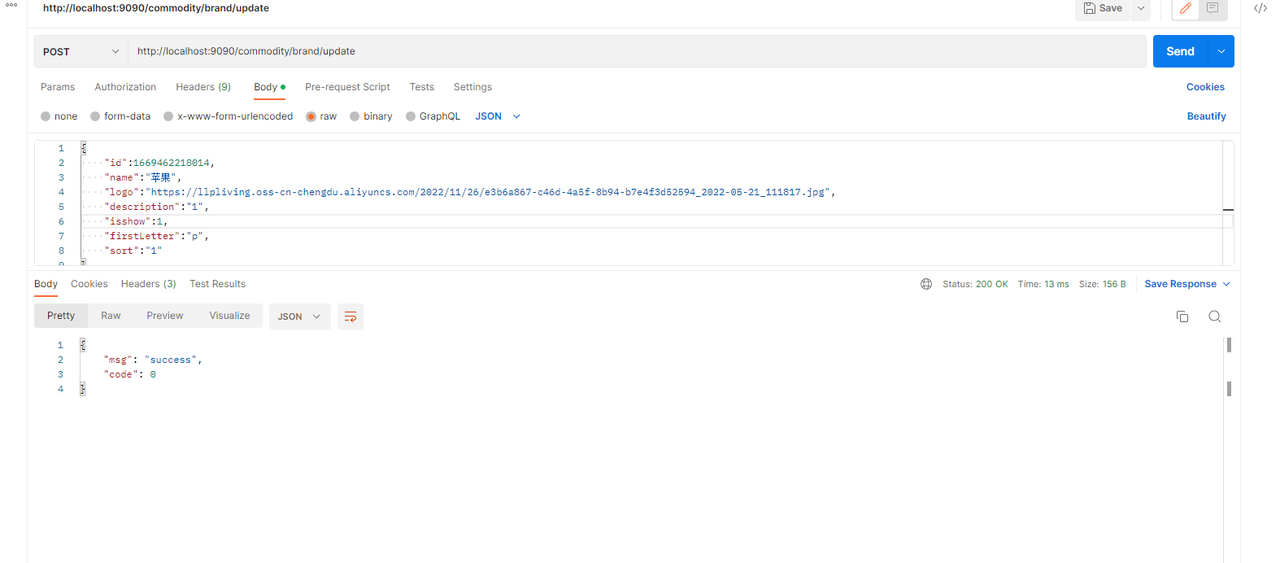
新增时,指定id。提示添加时不能指定id
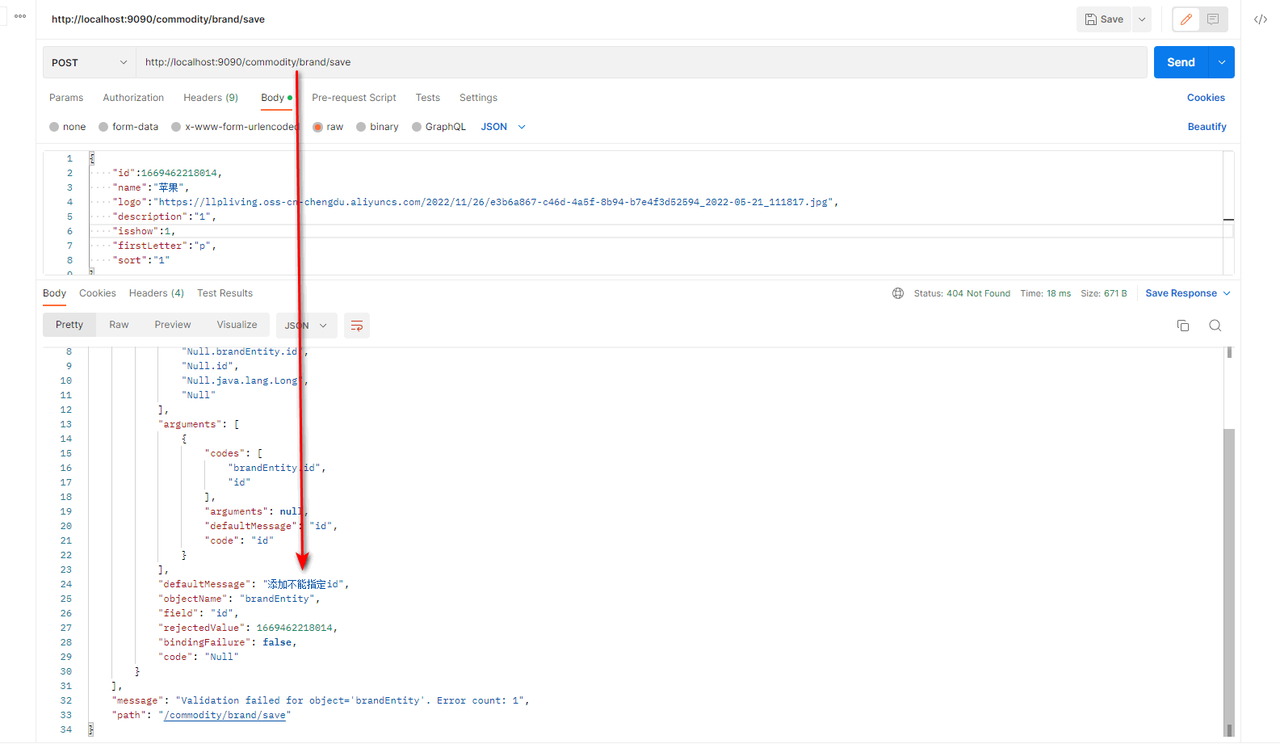
而修改时,指定id时可以的
3.自定义校验
引出自定义校验的必要性,为什么要使用自定义校验?
@NotNull(message = "显示状态不能为空",groups = {SaveGroup.class, UpdateGroup.class})
private Integer isshow;
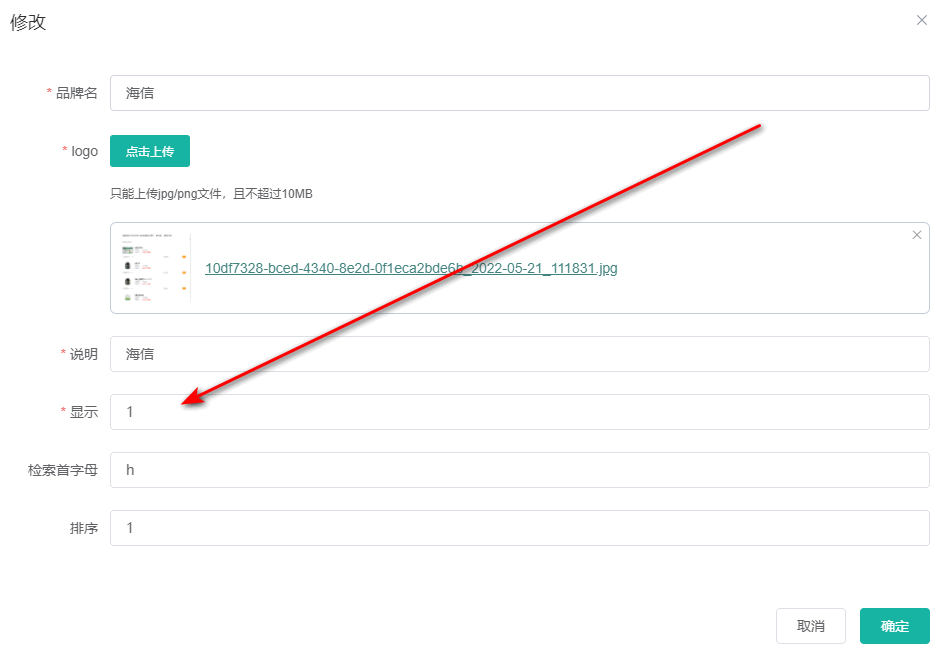
如上所示,针对是否显示做校验,比如我们想让1-表示显示,0-表示不显示。即isshow的值只能为0或者1。
当然前面提到的@Pattern注解可以实现这个功能,但@Pattern只能修饰字符串类型的字段。修饰其他字段则会抛出异常。因此如下代码是不成立的。
@NotNull(message = "显示状态不能为空",groups = {SaveGroup.class, UpdateGroup.class})
@Pattern(regexp = "^[0-1]$", message = "显示状态的值为0或1",groups = {SaveGroup.class, UpdateGroup.class})
private Integer isshow;
1.创建自定义校验注解
/**
* 1. EnumConstraintValidator是真正的校验器,即校验的逻辑是写在这里的
* 2. EnumConstraintValidator需要实现接口 ConstraintValidator
* 3. <EnumValidate,Integer> 表示该校验器是针对 @EnumValidate 传入的Integer类型数据进行校验
*/
@Target({ METHOD, FIELD, ANNOTATION_TYPE, CONSTRUCTOR, PARAMETER, TYPE_USE })
@Retention(RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Constraint(validatedBy = {EnumConstraintValidator.class})
public @interface EnumValidate {
/**
* 指定错误信息描述所在类的所在字段
* @return
*/
String message() default "{com.llp.common.valid.EnumValidate.message}";
/**
* 指定分组
* @return
*/
Class<?>[] groups() default { };
Class<? extends Payload>[] payload() default { };
//增加values属性
int[] values() default {};
//增加regexp
String regexp() default "";
}
2.自定义校验器
这里正则校验和数组元素校验存在重复,仅作为示例
/**
* 自定义校验器
*/
public class EnumConstraintValidator implements ConstraintValidator<EnumValidate, Integer> {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
private String regexp = "";
/**
* 初始化验证器,为isValid(Object, ConstraintValidatorContext)调用做准备。传递给定约束声明的约束注释。
* 保证在使用此实例进行验证之前调用此方法。 默认的实现是无操作的
*
* @param constraintAnnotation 自定义注解
*/
@Override
public void initialize(EnumValidate constraintAnnotation) {
int[] values = constraintAnnotation.values();
for (int value : values) {
set.add(value);
}
regexp = constraintAnnotation.regexp();
}
/**
* 如果返回true表示验证成功-通过
* 返回false,表示验证失败-没有通过
*
* @param value
* @param context
* @return
*/
@Override
public boolean isValid(Integer value, ConstraintValidatorContext context) {
boolean contains = set.contains(value);
if (!contains) {
return false;
}
if (!value.toString().matches(regexp)) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
3.自定义错误提示信息
在类路径resource目录下创建ValidationMessages.properties文件,“显示状态的值需要是0或者1”中文部分需转换为unicode码。
com.llp.common.valid.EnumValidate.message=显示状态的值需要是0或者1
4.在表单校验的类中添加自定义校验注解
@NotNull(message = "显示状态不能为空", groups = {SaveGroup.class, UpdateGroup.class})
@EnumValidate(values = {0, 1}, message = "显示只必须为1或者0", regexp = "^[0-1]$", groups = {SaveGroup.class, UpdateGroup.class})
private Integer isshow;
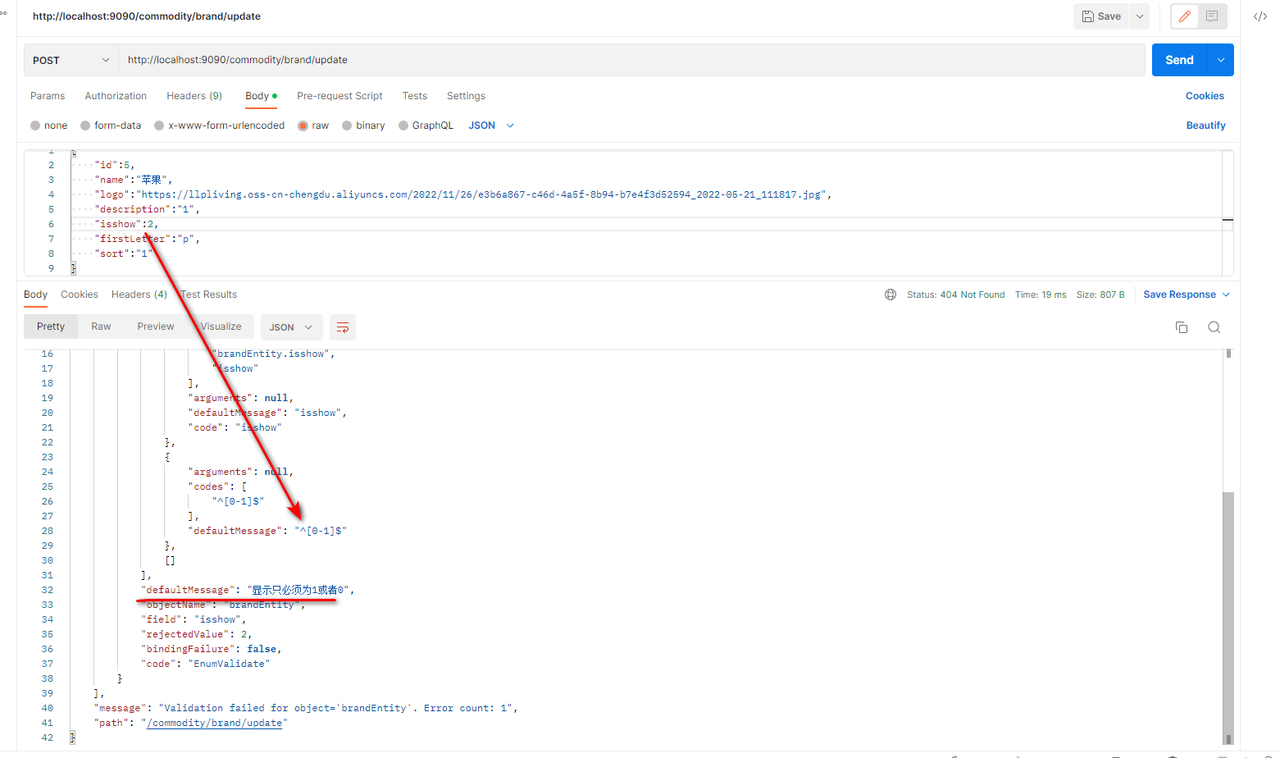
5.测试
可以看到针对isshow的校验信息,显示只必须为1或者0
3.注意事项和使用细节
-
一个自定义校验注解,可以由多个校验器来组合校验 ,如下
/** * 1. EnumConstraintValidator是真正的校验器,即校验的逻辑是写在这里的 * 2. EnumConstraintValidator需要实现接口 ConstraintValidator * 3. <EnumValidate,Integer> 表示该校验器是针对 @EnumValidate 传入的Integer类型数据进行校验 */ @Target({ METHOD, FIELD, ANNOTATION_TYPE, CONSTRUCTOR, PARAMETER, TYPE_USE }) @Retention(RUNTIME) @Documented @Constraint(validatedBy = {EnumConstraintValidator.class}) public @interface EnumValidate { /** * 指定错误信息描述所在类的所在字段 * @return */ String message() default "{com.llp.common.valid.EnumValidate.message}"; /** * 指定分组 * @return */ Class<?>[] groups() default { }; Class<? extends Payload>[] payload() default { }; //增加values属性 int[] values() default {}; //增加regexp String regexp() default ""; } -
注意, validatedBy = {EnumConstraintValidator.class} 是可以带校验器类型数组的.
 JavaSE
JavaSE
 JavaWeb
JavaWeb
 Spring
Spring
 MyBatis
MyBatis
 linux
linux
 消息队列
消息队列
 工具
工具
 片段
片段
 AI
AI
 搜索
搜索