中介者模式
中介者模式
1.中介者模式基本介绍
- 中介者模式(Mediator Pattern),用一个中介对象来封装一系列的对象交互。中介者使各个对象不需要显式地相互引用,从而使其耦合松散,而且可以独立地改变它们之间的交互
- 中介者模式属于行为型模式,使代码易于维护
- 比如 MVC 模式,C(Controller 控制器)是 M(Model 模型)和 V(View 视图)的中介者,在前后端交互时起到了中间人的作用
- 中介者模式的原理类图
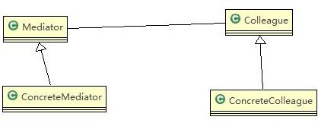
对原理类图的说明-即(中介者模式的角色及职责)
- Mediator 就是抽象中介者,定义了同事对象到中介者对象的接口
- Colleague 是抽象同事类
- ConcreteMediator 具体的中介者对象, 实现抽象方法, 他需要知道所有的具体的同事类,即以一个集合来管理
HashMap,并接受某个同事对象消息,完成相应的任务
- ConcreteColleague 具体的同事类,会有很多, 每个同事只知道自己的行为, 而不了解其他同事类的行为(方法), 但 是他们都依赖中介者对象
2.案例场景
智能家庭项目:
- 智能家庭包括各种设备,闹钟、咖啡机、电视机、窗帘 等
- 主人要看电视时,各个设备可以协同工作,自动完成看电视的准备工作,比如流程为:闹铃响起->咖啡机开始做咖啡->窗帘自动落下->电视机开始播放
- 传统方案解决智能家庭管理问题
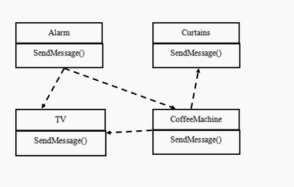
- 当各电器对象有多种状态改变时,相互之间的调用关系会比较复杂
- 各个电器对象彼此联系,你中有我,我中有你,不利于松耦合
- 各个电器对象之间所传递的消息(参数),容易混乱
- 当系统增加一个新的电器对象时,或者执行流程改变时,代码的可维护性、扩展性都不理想 考虑中介者模式
3.代码实现
完成前面的智能家庭的项目,使用中介者模式
思路分析和图解(类图)
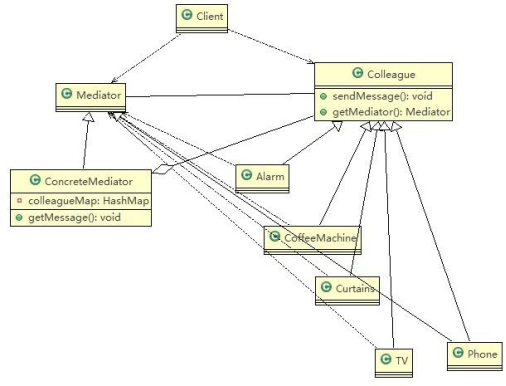
中介者接口
public abstract class Mediator {
//将给中介者对象,加入到集合中
public abstract void Register(String colleagueName, Colleague colleague);
//接收消息, 具体的同事对象发出
public abstract void GetMessage(int stateChange, String colleagueName);
public abstract void SendMessage();
}
具体的中介者类
//具体的中介者类
public class ConcreteMediator extends Mediator {
//集合,放入所有的同事对象
private HashMap<String, Colleague> colleagueMap;
private HashMap<String, String> interMap;
public ConcreteMediator() {
colleagueMap = new HashMap<String, Colleague>();
interMap = new HashMap<String, String>();
}
@Override
public void Register(String colleagueName, Colleague colleague) {
colleagueMap.put(colleagueName, colleague);
if (colleague instanceof Alarm) {
interMap.put("Alarm", colleagueName);
} else if (colleague instanceof CoffeeMachine) {
interMap.put("CoffeeMachine", colleagueName);
} else if (colleague instanceof TV) {
interMap.put("TV", colleagueName);
} else if (colleague instanceof Curtains) {
interMap.put("Curtains", colleagueName);
}
}
//具体中介者的核心方法
//1. 根据得到消息,完成对应任务
//2. 中介者在这个方法,协调各个具体的同事对象,完成任务
@Override
public void GetMessage(int stateChange, String colleagueName) {
//处理闹钟发出的消息
if (colleagueMap.get(colleagueName) instanceof Alarm) {
if (stateChange == 0) {
((CoffeeMachine) (colleagueMap.get(interMap
.get("CoffeeMachine")))).StartCoffee();
((TV) (colleagueMap.get(interMap.get("TV")))).StartTv();
} else if (stateChange == 1) {
((TV) (colleagueMap.get(interMap.get("TV")))).StopTv();
}
} else if (colleagueMap.get(colleagueName) instanceof CoffeeMachine) {
((Curtains) (colleagueMap.get(interMap.get("Curtains"))))
.UpCurtains();
} else if (colleagueMap.get(colleagueName) instanceof TV) {//如果TV发现消息
} else if (colleagueMap.get(colleagueName) instanceof Curtains) {
//如果是以窗帘发出的消息,这里处理...
}
}
@Override
public void SendMessage() {
}
}
同事抽象类
//同事抽象类
public abstract class Colleague {
private Mediator mediator;
public String name;
public Colleague(Mediator mediator, String name) {
this.mediator = mediator;
this.name = name;
}
public Mediator GetMediator() {
return this.mediator;
}
public abstract void SendMessage(int stateChange);
}
具体的同事类
//具体的同事类
public class Alarm extends Colleague {
//构造器
public Alarm(Mediator mediator, String name) {
super(mediator, name);
//在创建Alarm 同事对象时,将自己放入到ConcreteMediator 对象中[集合]
mediator.Register(name, this);
}
public void SendAlarm(int stateChange) {
SendMessage(stateChange);
}
@Override
public void SendMessage(int stateChange) {
//调用的中介者对象的getMessage
this.GetMediator().GetMessage(stateChange, this.name);
}
}
public class TV extends Colleague {
public TV(Mediator mediator, String name) {
super(mediator, name);
mediator.Register(name, this);
}
@Override
public void SendMessage(int stateChange) {
this.GetMediator().GetMessage(stateChange, this.name);
}
public void StartTv() {
System.out.println("It's time to StartTv!");
}
public void StopTv() {
System.out.println("StopTv!");
}
}
public class Curtains extends Colleague {
public Curtains(Mediator mediator, String name) {
super(mediator, name);
mediator.Register(name, this);
}
@Override
public void SendMessage(int stateChange) {
this.GetMediator().GetMessage(stateChange, this.name);
}
public void UpCurtains() {
System.out.println("I am holding Up Curtains!");
}
}
测试类
public class ClientTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个中介者对象
Mediator mediator = new ConcreteMediator();
//创建Alarm 并且加入到 ConcreteMediator 对象的HashMap
Alarm alarm = new Alarm(mediator, "alarm");
//创建了CoffeeMachine 对象,并 且加入到 ConcreteMediator 对象的HashMap
CoffeeMachine coffeeMachine = new CoffeeMachine(mediator,
"coffeeMachine");
//创建 Curtains , 并 且加入到 ConcreteMediator 对象的HashMap
Curtains curtains = new Curtains(mediator, "curtains");
TV tV = new TV(mediator, "TV");
//让闹钟发出消息
alarm.SendAlarm(0);
coffeeMachine.FinishCoffee();
alarm.SendAlarm(1);
}
}
测试结果
It's time to startcoffee!
It's time to StartTv!
After 5 minutes!
Coffee is ok!
I am holding Up Curtains!
StopTv!
4.中介者模式的注意事项和细节
- 多个类相互耦合,会形成网状结构, 使用中介者模式将网状结构分离为星型结构,进行解耦
- 减少类间依赖,降低了耦合,符合迪米特原则
- 中介者承担了较多的责任,一旦中介者出现了问题,整个系统就会受到影响
- 如果设计不当,中介者对象本身变得过于复杂,这点在实际使用时,要特别注意
 JavaSE
JavaSE
 JavaWeb
JavaWeb
 Spring
Spring
 MyBatis
MyBatis
 linux
linux
 消息队列
消息队列
 工具
工具
 片段
片段
 AI
AI
 搜索
搜索