阿里云短信服务
一、阿里云短信服务开通
1.阿里云短信说明
https://dysms.console.aliyun.com/overview
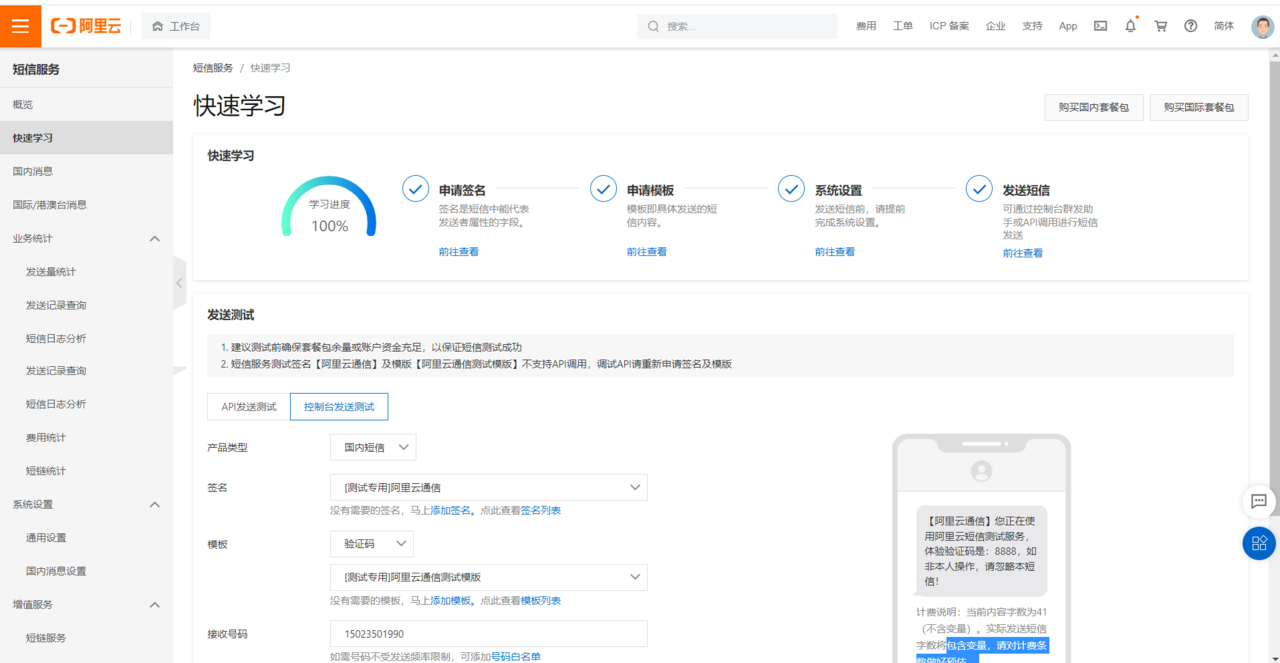
登录访问阿里云短信服务,可以看到大致的操作步骤:
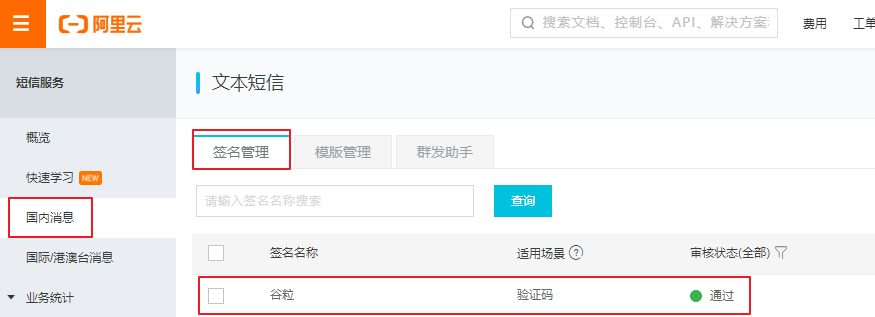
1.申请签名,如:【阿里云短信】
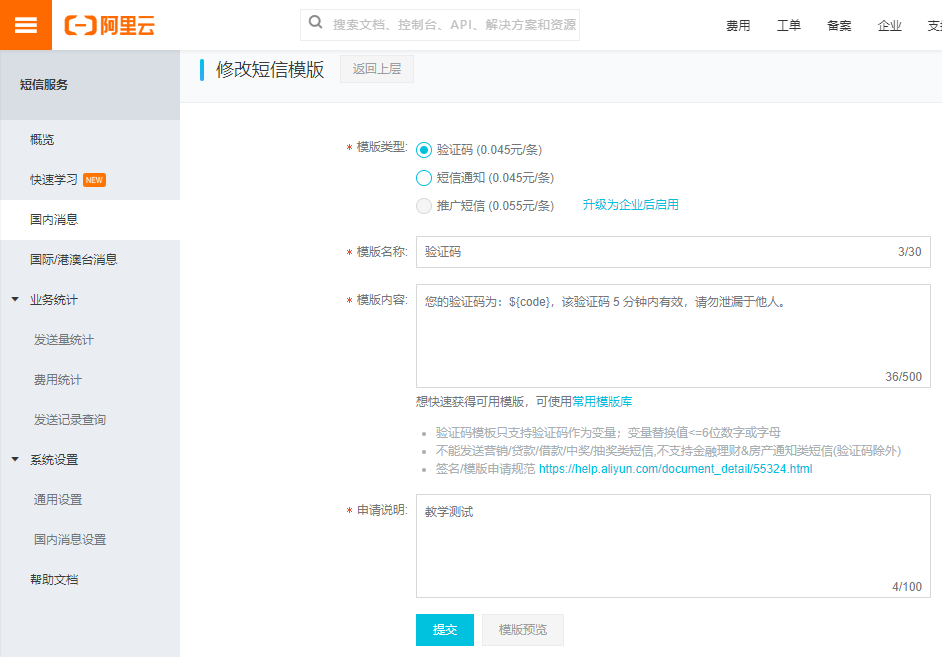
2.申请模板,如:【阿里云通信】您正在使用阿里云短信测试服务,体验验证码是:8888,如非本人操作,请忽略本短信!
3.系统设置,状态报告,审核通知,上行消息接收等
4.发送短信
阿里云提供了验证码的发送测试,我们可以通过测试发送短信到手机上查看效果。
通过下图我们可以看到阿里云发送消息分为国内消息和国际/港澳台消息两个类型,两者都需要单独申请签名模板才能发送。本文已国内消息下发为例,国际消息同理。
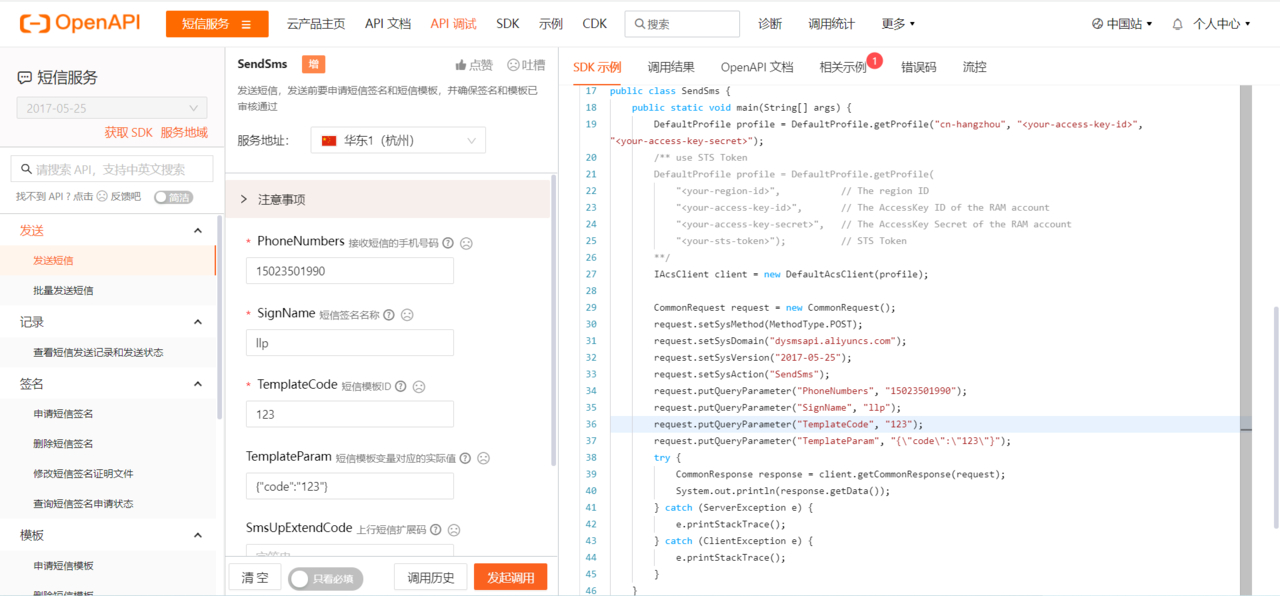
APIDemo
2.接入阿里云短信
2.1RAM访问控制添加用户
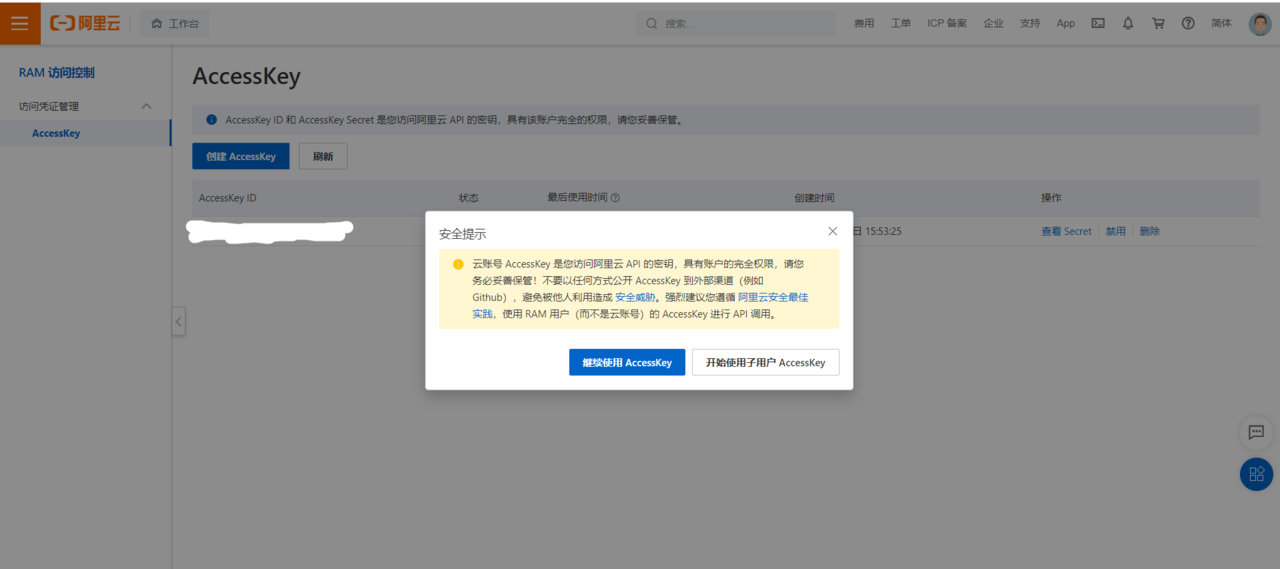
AccessKey和子用户AccessKey的区别在于AccessKey账户具备所有权限而子用户AccessKey需要手动添加。
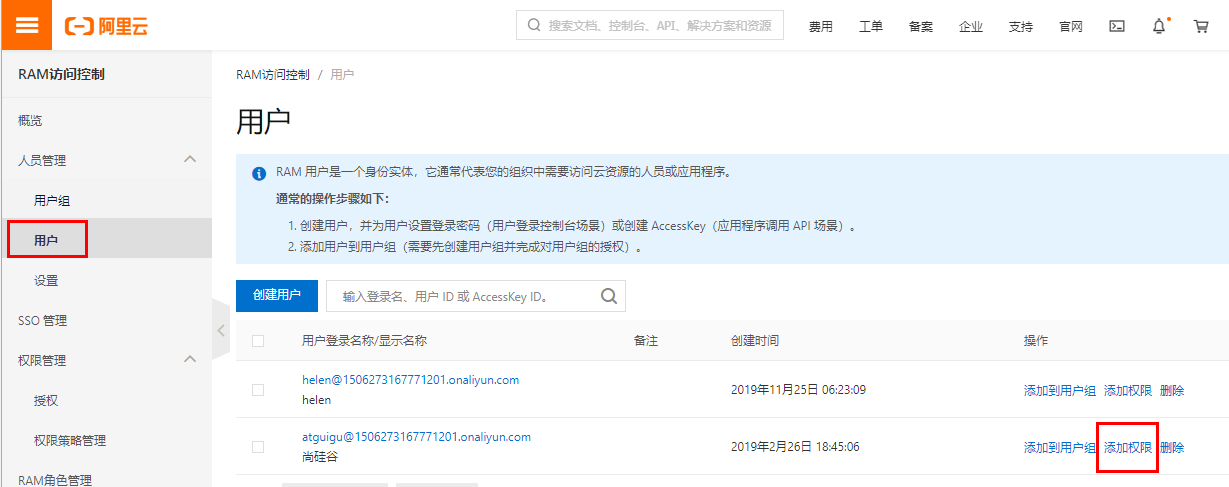
这里我选择的是子账户进入之后添加新增用户如下,我们创建这个账户后续通过接口的方式调用阿里短信服务发送短信,所以这里一定要勾选OpenApI通用访问。
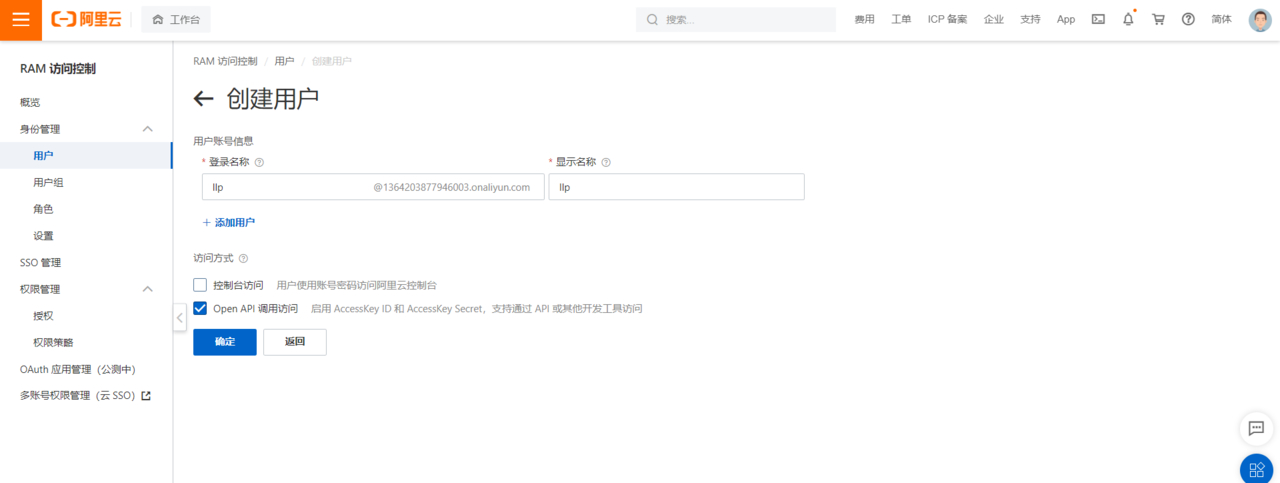
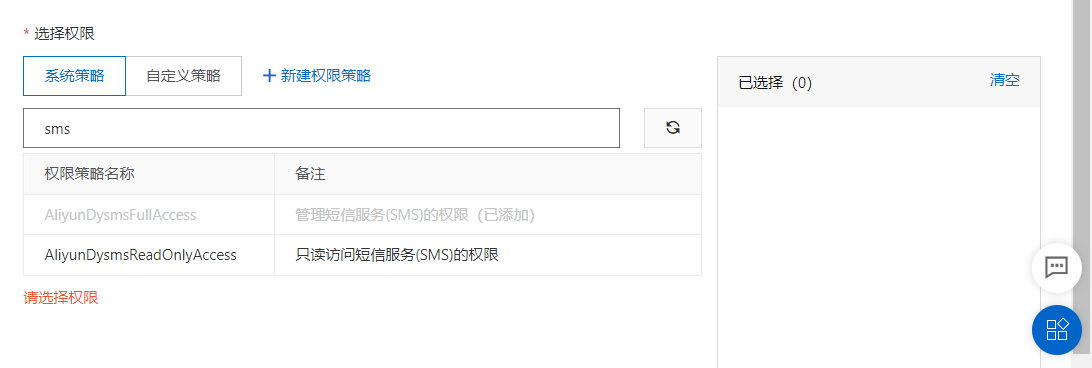
添加账户成功之后我们需要给子账户分配权限,授权:AliyunDysmsFullAccess
开通账户之后,一定要记录下AccessKeyId, AccessKeySecret便于后续使用
3.开通短信服务
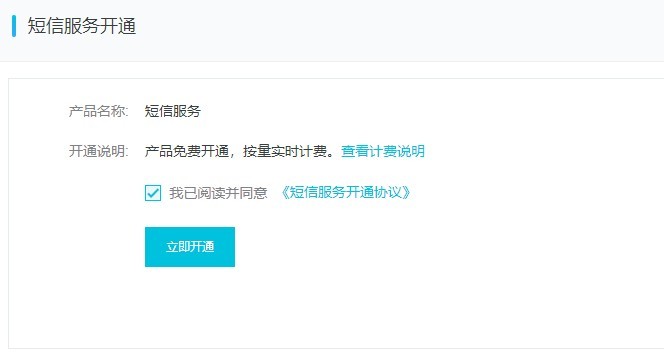
3.1、开通
3.2、添加签名
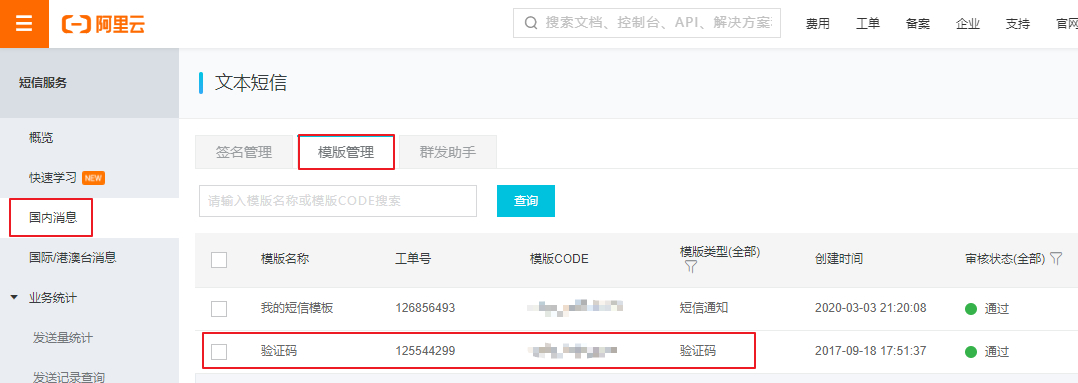
3.3、添加模板
3.4、套餐
free.aliyun.com 提供了免费试用的服务,如果只是平时学习测试的化,可以通过该网站申请免费试用
3.5快速学习

4.测试短信发送
4.1、查找使用示例
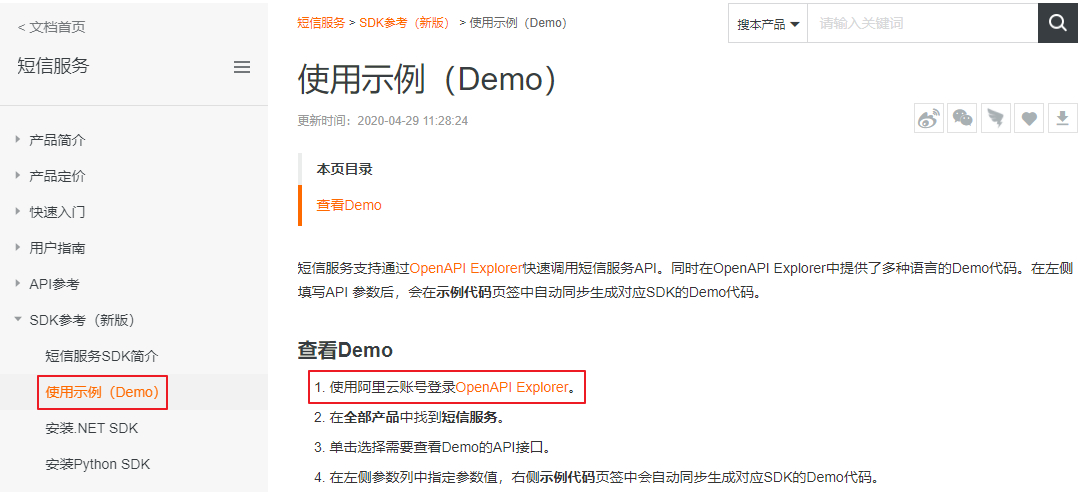
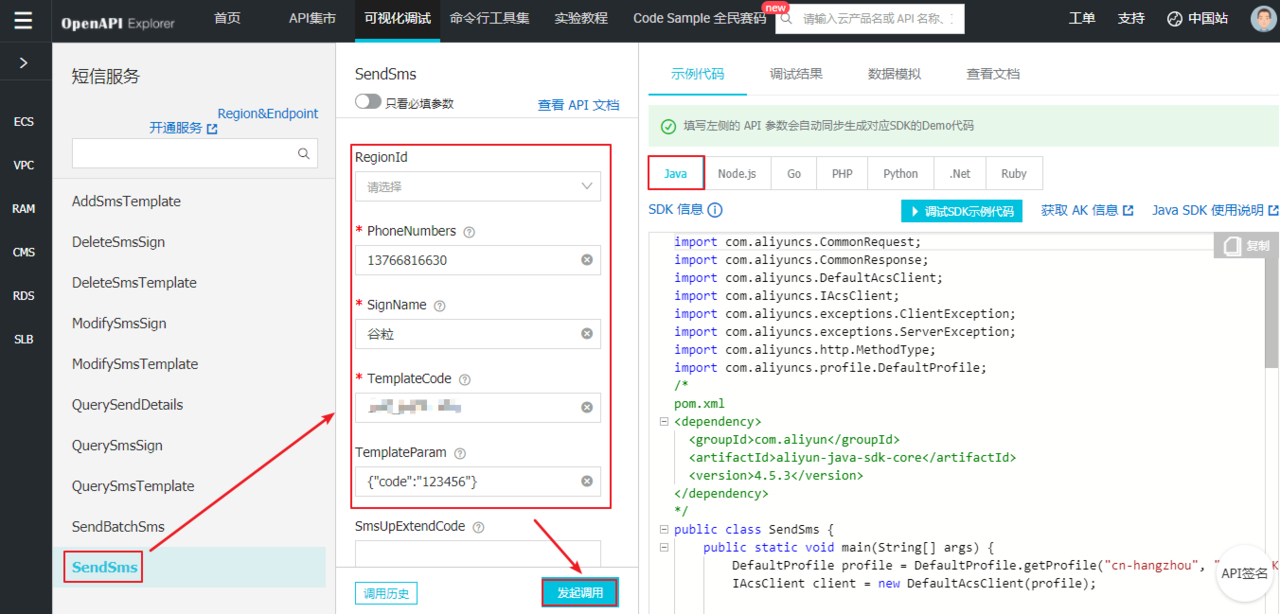
4.2、测试短信发送

4.3、查看发送结果
短信服务->业务统计->发送记录查询
二、阿里云短信服务开发
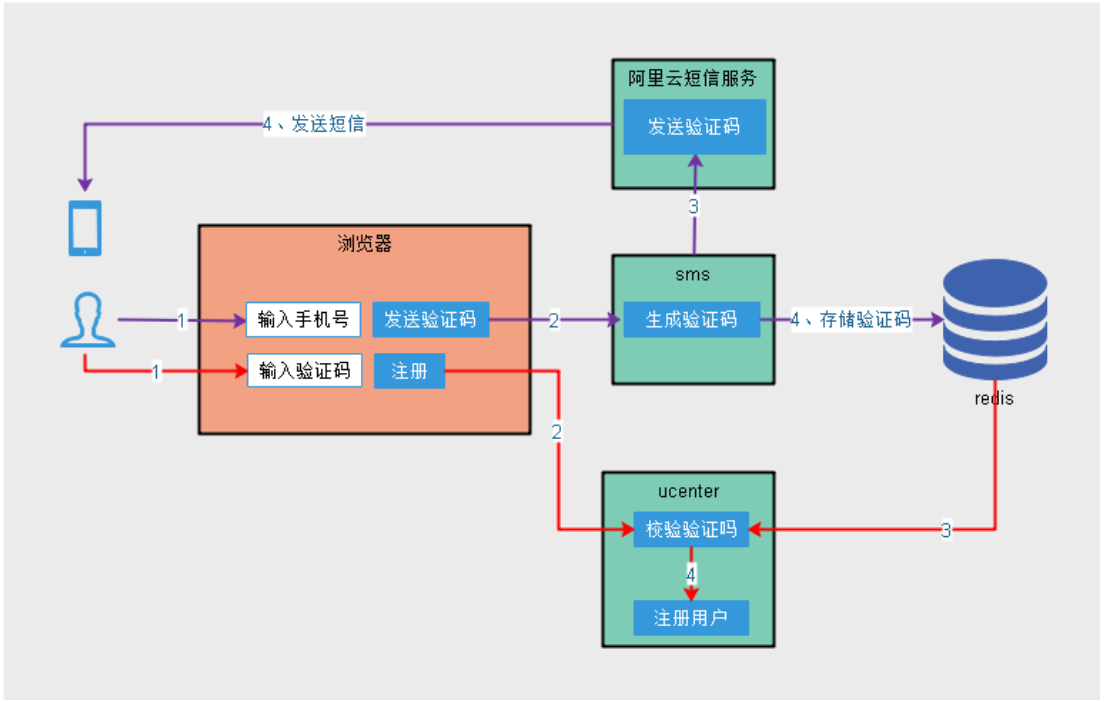
在日常开发中短信服务主要应用于用户验证码获取、已经消息通知等业务。这里已用户通过手机号获取验证码注册账号为例。
验证码获取业务流程
1.基础配置
<!--阿里云短信-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.aliyun</groupId>
<artifactId>aliyun-java-sdk-core</artifactId>
</dependency>
#阿里云短信
aliyun:
sms:
region-id: cn-hangzhou
key-id: 你的appId
key-secret: 你的appkey
template-code: 你的模板id
sign-name: 你的签名
1.这里配置类实现InitializingBean接口实现afterPropertiesSet方法,当Spring容器将regionId、keyId、keySecret等参数赋值之后,程序会调用afterPropertiesSet方法我们可以将配置的值赋值给常量,这样我们就可以通过类名.常量名去获取值了。
2.通过下面的配置我们在application.yml就可以提示我们配置类自己定义的变量,这样我们可以先定义配置类在写application.yml中的配置
配置类
@Data
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(value = "aliyun.sms")
public class SmsProperties implements InitializingBean {
private String regionId;
private String keyId;
private String keySecret;
private String templateCode;
private String signName;
public static String REGION_Id;
public static String KEY_ID;
public static String KEY_SECRET;
public static String TEMPLATE_CODE;
public static String SIGN_NAME;
//当私有成员被赋值后,此方法自动被调用,从而初始化常量
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
REGION_Id = regionId;
KEY_ID = keyId;
KEY_SECRET = keySecret;
TEMPLATE_CODE = templateCode;
SIGN_NAME = signName;
}
}
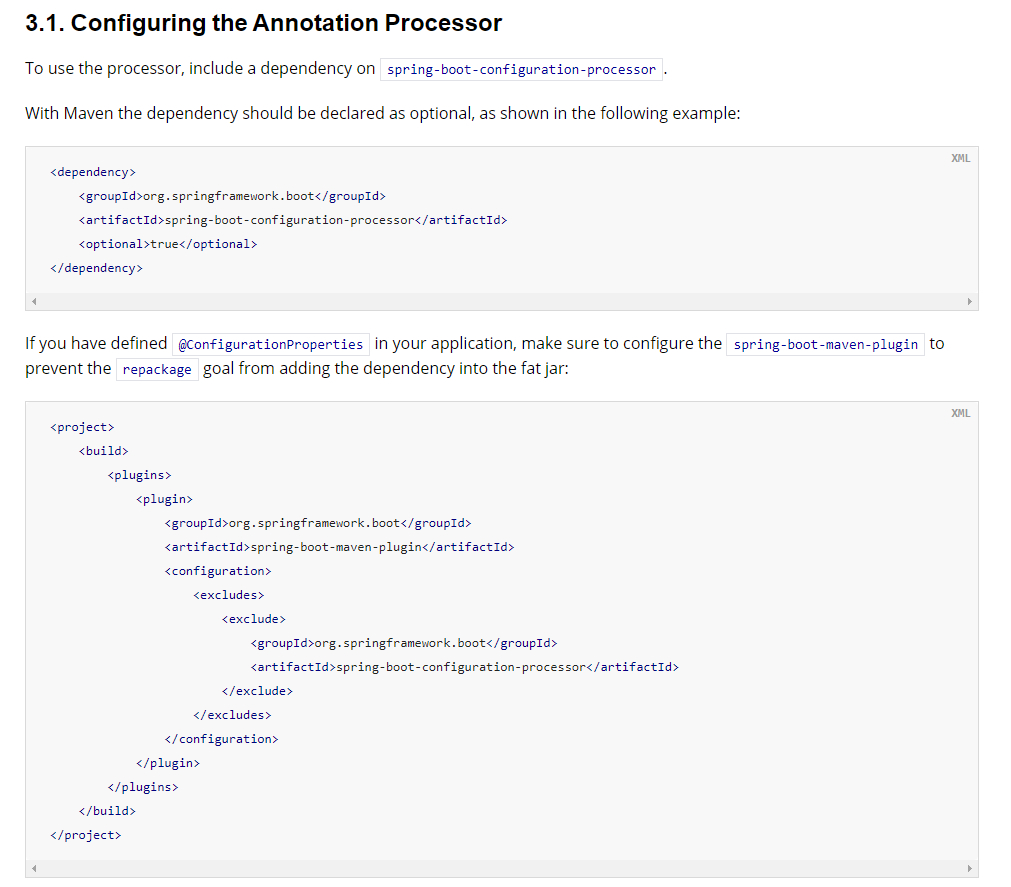
Idea报告如下错误信息(不影响程序的编译和运行):

解决方案参考文档:
controller层
@ApiOperation("获取验证码")
@GetMapping("/send/{mobile}")
public R send(@ApiParam(value = "手机号码", required = true)
@PathVariable String mobile) {
//手机号码不能为空
Assert.notEmpty(mobile, ResponseEnum.MOBILE_NULL_ERROR);
//手机号码是否合法
Assert.isTrue(RegexValidateUtils.checkCellphone(mobile), ResponseEnum.MOBILE_ERROR);
//手机号是否被注册过
boolean result = coreUserInfoClient.checkMobile(mobile);
Assert.isTrue(result==false,ResponseEnum.MOBILE_EXIST_ERROR);
//生成验证码
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
String code = RandomUtils.getFourBitRandom();
log.info("验证码:{}",code);
map.put("code", code);
//发送阿里云短信验证码
smsService.send(mobile, SmsProperties.TEMPLATE_CODE,map);
//发送短信验证码
// rlySmsService.send(mobile, RLYSmsProperties.TEMPLATE_ID, map);
//将验证码存入redis中
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("srb:mms:code:" + mobile, code);
return R.ok().message("获取验证码成功").data("code",code);
}
service层
发送短信的代码基本基本从demo中拷贝出来,我们只需要定义短信模板中的几个变量就可以了。
@Override
public void send(String mobile, String templateCode, Map<String, Object> param) {
//创建远程连接客户端对象
DefaultProfile profile = DefaultProfile.getProfile(
SmsProperties.REGION_Id,
SmsProperties.KEY_ID,
SmsProperties.KEY_SECRET);
IAcsClient client = new DefaultAcsClient(profile);
//创建远程连接的请求参数
CommonRequest request = new CommonRequest();
request.setSysMethod(MethodType.POST);
request.setSysDomain("dysmsapi.aliyuncs.com");
request.setSysVersion("2017-05-25");
request.setSysAction("SendSms");
request.putQueryParameter("RegionId", SmsProperties.REGION_Id);
request.putQueryParameter("PhoneNumbers", mobile);
request.putQueryParameter("SignName", SmsProperties.SIGN_NAME);
request.putQueryParameter("TemplateCode", templateCode);
Gson gson = new Gson();
String json = gson.toJson(param);
request.putQueryParameter("TemplateParam", json);
try {
//使用客户端对象携带请求对象发送请求并得到响应结果
CommonResponse response = client.getCommonResponse(request);
boolean success = response.getHttpResponse().isSuccess();
//ALIYUN_RESPONSE_FAIL(-501, "阿里云响应失败"),
Assert.isTrue(success, ResponseEnum.ALIYUN_RESPONSE_FAIL);
String data = response.getData();
HashMap<String, String> resultMap = gson.fromJson(data, HashMap.class);
String code = resultMap.get("Code");
String message = resultMap.get("Message");
log.info("阿里云短信发送响应结果:");
log.info("code:" + code);
log.info("message:" + message);
//ALIYUN_SMS_LIMIT_CONTROL_ERROR(-502, "短信发送过于频繁"),//业务限流
Assert.notEquals("isv.BUSINESS_LIMIT_CONTROL", code, ResponseEnum.ALIYUN_SMS_LIMIT_CONTROL_ERROR);
//ALIYUN_SMS_ERROR(-503, "短信发送失败"),//其他失败
Assert.equals("OK", code, ResponseEnum.ALIYUN_SMS_ERROR);
} catch (ServerException e) {
log.error("阿里云短信发送SDK调用失败:");
log.error("ErrorCode=" + e.getErrCode());
log.error("ErrorMessage=" + e.getErrMsg());
throw new BusinessException(ResponseEnum.ALIYUN_SMS_ERROR, e);
} catch (ClientException e) {
log.error("阿里云短信发送SDK调用失败:");
log.error("ErrorCode=" + e.getErrCode());
log.error("ErrorMessage=" + e.getErrMsg());
throw new BusinessException(ResponseEnum.ALIYUN_SMS_ERROR, e);
}
}
2. 4-6位随机生成工具类
/**
* 生成四位和六位的随机数字
*/
public class RandomUtils {
private static final Random random = new Random();
private static final DecimalFormat fourdf = new DecimalFormat("0000");
private static final DecimalFormat sixdf = new DecimalFormat("000000");
public static String getFourBitRandom() {
return fourdf.format(random.nextInt(10000));
}
public static String getSixBitRandom() {
return sixdf.format(random.nextInt(1000000));
}
/**
* 给定数组,抽取n个数据
* @param list
* @param n
* @return
*/
public static ArrayList getRandom(List list, int n) {
Random random = new Random();
HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap = new HashMap<Object, Object>();
// 生成随机数字并存入HashMap
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
int number = random.nextInt(100) + 1;
hashMap.put(number, i);
}
// 从HashMap导入数组
Object[] robjs = hashMap.values().toArray();
ArrayList r = new ArrayList();
// 遍历数组并打印数据
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
r.add(list.get((int) robjs[i]));
System.out.print(list.get((int) robjs[i]) + "\t");
}
System.out.print("\n");
return r;
}
}
 JavaSE
JavaSE
 JavaWeb
JavaWeb
 Spring
Spring
 MyBatis
MyBatis
 linux
linux
 消息队列
消息队列
 工具
工具
 片段
片段
 AI
AI
 搜索
搜索