IO流
IO流
1.0 文件
什么是文件

1.1 文件流
输入流和输出流根据程序来判定:
1.从程序中写出就是输出流
2.写入程序中就是输入流

1.2常用的文件操作
1.2.1创建文件对象相关构造器和方法
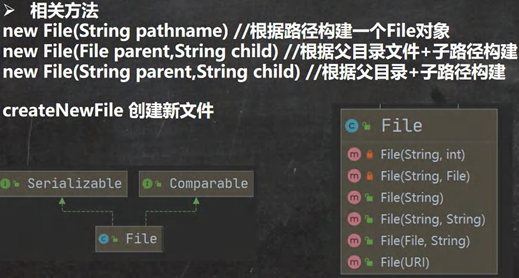
public class FileCreate {
@Test
public void create01() throws IOException {
String filePath = "C:\\Users\\asus\\Desktop\\io\\1.txt";
File file = new File(filePath);
if(!file.exists()){
file.createNewFile();
}
System.out.println(file.getName()+"文件创建成功");
}
@Test
public void create02() throws IOException {
File fileParent = new File("C:\\Users\\asus\\Desktop\\io");
String Child = "2.txt";
File file = new File(fileParent, Child);
file.createNewFile();
System.out.println(file.getName()+"文件创建成功");
}
@Test
public void create03() throws IOException {
String fileParentPath = "C:\\Users\\asus\\Desktop\\io";
String child = "3.txt";
File file = new File(fileParentPath, child);
file.createNewFile();
System.out.println(file.getName()+"文件创建成功");
}
}
1.2.2获取文件的相关信息

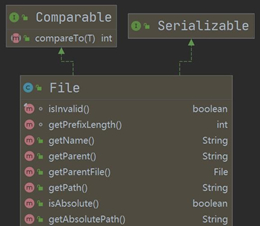
//获取文件的信息
@Test
public void info() {
//先创建文件对象
File file = new File("e:\\news1.txt");
//调用相应的方法,得到对应信息
System.out.println("文件名字=" + file.getName());
//getName、getAbsolutePath、getParent、length、exists、isFile、isDirectory
System.out.println("文件绝对路径=" + file.getAbsolutePath());
System.out.println("文件父级目录=" + file.getParent());
System.out.println("文件大小(字节)=" + file.length());
System.out.println("文件是否存在=" + file.exists());//T
System.out.println("是不是一个文件=" + file.isFile());//T
System.out.println("是不是一个目录=" + file.isDirectory());//F
}
1.2.3 目录的操作和文件删除
public class Directory_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String directoryPath = "C:\\Users\\asus\\Desktop\\io";
// Directory_.recursionDeleteFile(new File(directoryPath));
Directory_.recursionGetFile(new File(directoryPath));
}
//删除文件
@Test
public void m1(){
String filePath = "C:\\Users\\asus\\Desktop\\io\\1.txt";
File file = new File(filePath);
if(file.exists()){
if (file.delete()) {
System.out.println(filePath + "删除成功");
} else {
System.out.println(filePath + "删除失败");
}
}else {
System.out.println("该文件不存在");
}
}
//删除目录:目录删除只能逐级删除且必须是空目录
@Test void m2(){
String filePath = "C:\\Users\\asus\\Desktop\\io";
File file = new File(filePath);
if(file.exists()){
if (file.delete()) {
System.out.println(filePath + "删除成功");
} else {
System.out.println(filePath + "删除失败");
}
} else {
System.out.println("该目录不存在...");
}
}
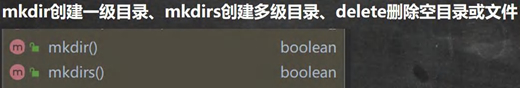
//创建目录
@Test
public void m3() {
String directoryPath = "C:\\Users\\asus\\Desktop\\a\\b\\c\\d";
File file = new File(directoryPath);
if (file.exists()) {
System.out.println(directoryPath + "存在..");
} else {
if (file.mkdirs()) { //创建一级目录使用mkdir() ,创建多级目录使用mkdirs()
System.out.println(directoryPath + "创建成功..");
} else {
System.out.println(directoryPath + "创建失败...");
}
}
}
//递归删除文件下的子目录和子文件
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public static void recursionDeleteFile(File file){
//此方法只做两件事:1.如果是文件,直接删除2.如果是文件夹,获取文件夹的子元素。循环遍历
if (file.exists()) {
if (file.isFile()) {//是否是文件
file.delete();//删除文件
System.out.println(file.getName()+"已删除");
}else {
File f[]=file.listFiles();//获取目录的子目录、子文件File数组
for (int i = 0; i < f.length; i++) {
recursionDeleteFile(f[i]);//方法递归
}
file.delete();//删除父级空文件夹
}
}else {
System.out.println("文件不存在");
}
}
//递归获取目录下的所有文件
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public static void recursionGetFile(File file){
//此方法只做两件事:1.如果是文件,直接删除2.如果是文件夹,获取文件夹的子元素。循环遍历
if (file.exists()) {
if (file.isFile()) {//是否是文件
System.out.println(file.getName());
}else {
File f[]=file.listFiles();//获取目录的子目录、子文件File数组
for (int i = 0; i < f.length; i++) {
recursionGetFile(f[i]);//方法递归
}
}
}else {
System.out.println("文件不存在");
}
}
}
1.3 IO流原理及流的分类
1.3.1 Java IO流原理


InputStream
OutputStream
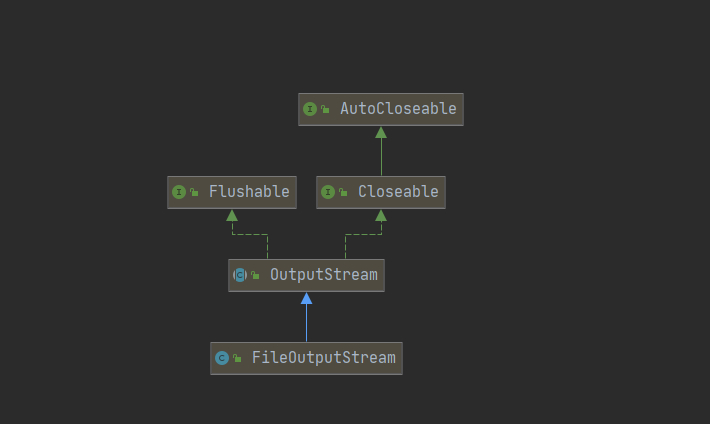
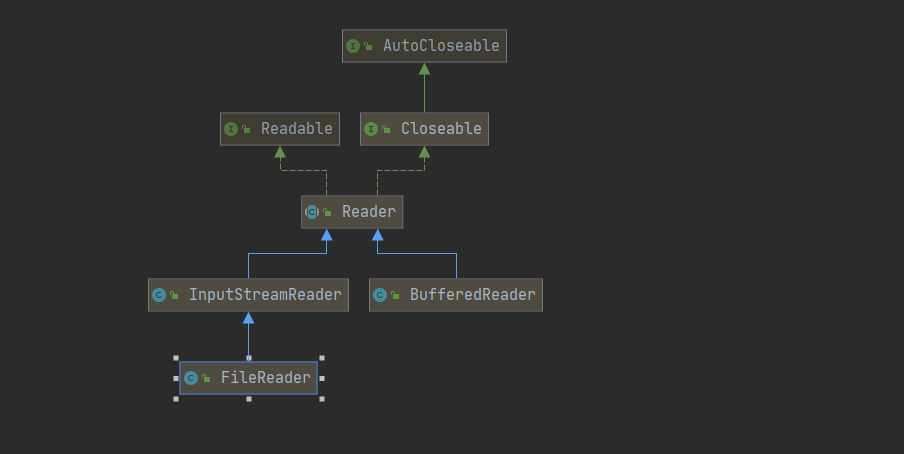
FileReader
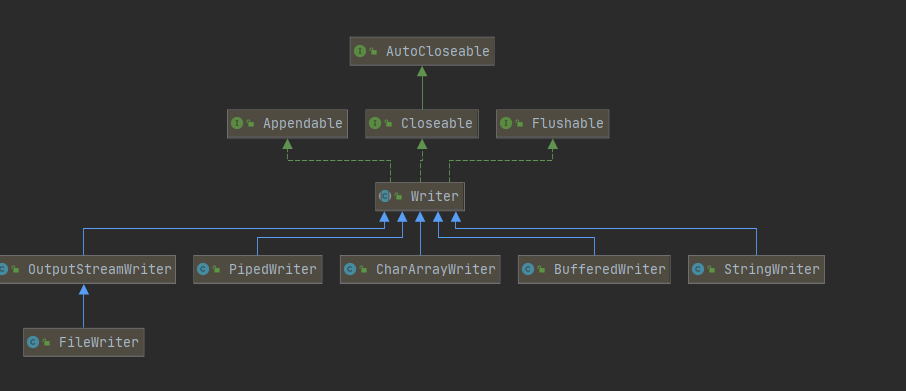
FileWriter
1.3.2 流的分类
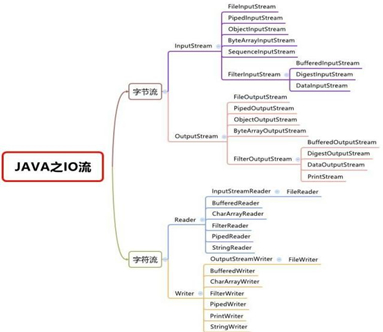
IO按照数据单位划分为:
1.字节流 ;常用于音频、视频文件能够防止文件数据丢失
2.字符流; 常用于文本文件,效率较高
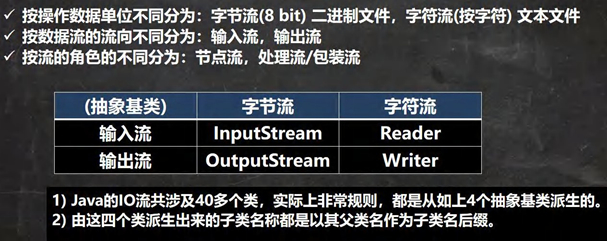
1.4 IO流体系图-常用的类
体系图
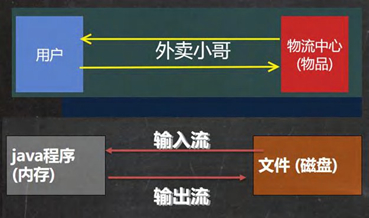
文件VS流
1.4.1 FileInputStream 介绍
/**
* 演示读取文件...
* 单个字节的读取,效率比较低
* -> 使用 read(byte[] b)
*/
@Test
public void readFile01() {
String filePath = "C:\\Users\\asus\\Desktop\\io\\2.txt";
int readData = 0;
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
try {
//创建 FileInputStream 对象,用于读取 文件
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(filePath);
//从该输入流读取一个字节的数据。 如果没有输入可用,此方法将阻止。
//如果返回-1 , 表示读取完毕
while ((readData = fileInputStream.read()) != -1) {
//当读取的文件含有中文是会出现乱码,因为每次只读取一个字节,不能读取完一个完整的汉字
System.out.print((char)readData);//转成char显示
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//关闭文件流,释放资源.
try {
fileInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 使用 read(byte[] b) 读取文件,提高效率
*/
@Test
public void readFile02() {
String filePath = "C:\\Users\\asus\\Desktop\\io\\2.txt";
//字节数组
byte[] buf = new byte[8]; //一次读取8个字节.
int readLen = 0;
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
try {
//创建 FileInputStream 对象,用于读取 文件
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(filePath);
//从该输入流读取最多b.length字节的数据到字节数组。 此方法将阻塞,直到某些输入可用。
//如果返回-1 , 表示读取完毕
//如果读取正常, 返回实际读取的字节数
while ((readLen = fileInputStream.read(buf)) != -1) {
//一次性读取多个字节是,可以避免一部分中文乱码问题,但问题依然存在
System.out.print(new String(buf, 0, readLen));//显示
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//关闭文件流,释放资源.
try {
fileInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
1.4.2FileOutputStream介绍
public class FileOutputStream01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
/**
* 演示使用FileOutputStream 将数据写到文件中,
* 如果该文件不存在,则创建该文件
*/
@Test
public void writeFile() {
//创建 FileOutputStream对象
String filePath = "C:\\Users\\asus\\Desktop\\a\\1.txt";
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
try {
//得到 FileOutputStream对象 对象
//老师说明
//1. new FileOutputStream(filePath) 创建方式,当写入内容是,会覆盖原来的内容
//2. new FileOutputStream(filePath, true) 创建方式,当写入内容是,是追加到文件后面
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(filePath, false);
//写入一个字节
//fileOutputStream.write('H');//
//写入字符串
String str = "孙悟空,world!";
//str.getBytes() 可以把 字符串-> 字节数组
// fileOutputStream.write(str.getBytes(Charset.forName("UTF-8")));
/*
write(byte[] b, int off, int len) 将 len字节从位于偏移量 off的指定字节数组写入此文件输出流
*/
// System.out.println(str.length());
// fileOutputStream.write(str.getBytes(), 0, str.length());
fileOutputStream.write(str.getBytes(), 0, str.getBytes().length);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
fileOutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
1.4.3文件拷贝FileCopy
文件拷贝实际上是将一个文件写入程序,再将程序写入另一个文件的过程
public class FileCopy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//完成 文件拷贝,将 e:\\Koala.jpg 拷贝 c:\\
//思路分析
//1. 创建文件的输入流 , 将文件读入到程序
//2. 创建文件的输出流, 将读取到的文件数据,写入到指定的文件.
String srcFilePath = "C:\\Users\\asus\\Desktop\\a\\1.txt"; //原文件
String destFilePath = "C:\\Users\\asus\\Desktop\\b\\1.txt"; //拷贝的文件
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
try {
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(srcFilePath);
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(destFilePath);
//定义一个字节数组,提高读取效果
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int readLen = 0;
while ((readLen = fileInputStream.read(buf)) != -1) {
//读取到后,就写入到文件 通过 fileOutputStream
//即,是一边读,一边写
fileOutputStream.write(buf, 0, readLen);//一定要使用这个方法
}
System.out.println("拷贝ok~");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
//关闭输入流和输出流,释放资源
if (fileInputStream != null) {
fileInputStream.close();
}
if (fileOutputStream != null) {
fileOutputStream.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
1.4.4 FileReader和FileWriter介绍
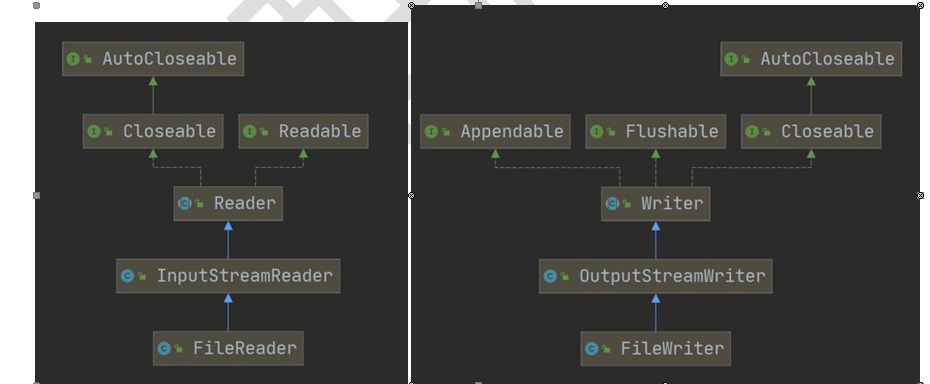
FileReader常用方法

/**
* 单个字符读取文件
*/
@Test
public void readFile01() {
String filePath = "C:\\Users\\asus\\Desktop\\b\\1.txt";
FileReader fileReader = null;
int data = 0;
//1. 创建FileReader对象
try {
fileReader = new FileReader(filePath);
//循环读取 使用read, 单个字符读取
while ((data = fileReader.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char) data);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (fileReader != null) {
fileReader.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 字符数组读取文件
*/
@Test
public void readFile02() {
System.out.println("~~~readFile02 ~~~");
String filePath = "C:\\Users\\asus\\Desktop\\b\\1.txt";
FileReader fileReader = null;
int readLen = 0;
char[] buf = new char[8];
//1. 创建FileReader对象
try {
fileReader = new FileReader(filePath);
//循环读取 使用read(buf), 返回的是实际读取到的字符数
//如果返回-1, 说明到文件结束
while ((readLen = fileReader.read(buf)) != -1) {
System.out.print(new String(buf, 0, readLen));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (fileReader != null) {
fileReader.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
FileWriter常用方法

public class FileWriter_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filePath = "C:\\Users\\asus\\Desktop\\b\\note.txt";
//创建FileWriter对象
FileWriter fileWriter = null;
char[] chars = {'a', 'b', 'c'};
try {
fileWriter = new FileWriter(filePath);//默认是覆盖写入
// 3) write(int):写入单个字符
fileWriter.write('H');
// 4) write(char[]):写入指定数组
fileWriter.write(chars);
// 5) write(char[],off,len):写入指定数组的指定部分
fileWriter.write("韩顺平教育".toCharArray(), 0, 3);
// 6) write(string):写入整个字符串
fileWriter.write(" 你好北京~");
fileWriter.write("风雨之后,定见彩虹");
// 7) write(string,off,len):写入字符串的指定部分
fileWriter.write("上海天津", 0, 2);
//这里fileWriter为同一个对象,所有最新写入内容是将依次连接起来的
//fileWriter(filePath,append)中append设置为true时会在后面添加
//在数据量大的情况下,可以使用循环操作.
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//对应FileWriter , 一定要关闭流,或者flush才能真正的把数据写入到文件
//老韩看源码就知道原因.
/*
看看代码
private void writeBytes() throws IOException {
this.bb.flip();
int var1 = this.bb.limit();
int var2 = this.bb.position();
assert var2 <= var1;
int var3 = var2 <= var1 ? var1 - var2 : 0;
if (var3 > 0) {
if (this.ch != null) {
assert this.ch.write(this.bb) == var3 : var3;
} else {
this.out.write(this.bb.array(), this.bb.arrayOffset() + var2, var3);
}
}
this.bb.clear();
}
*/
try {
//fileWriter.flush();
//关闭文件流,等价 flush() + 关闭
fileWriter.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("程序结束...");
}
}
1.5 节点流和处理流
1.5.1 基本介绍

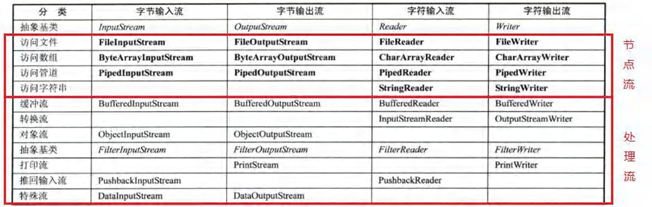
1.5.2节点流和处理流的区别和联系

下图中Reader是一个抽象类,而BufferedReader与其他之类不同在于构造器中定义了父类Reader类型的字段
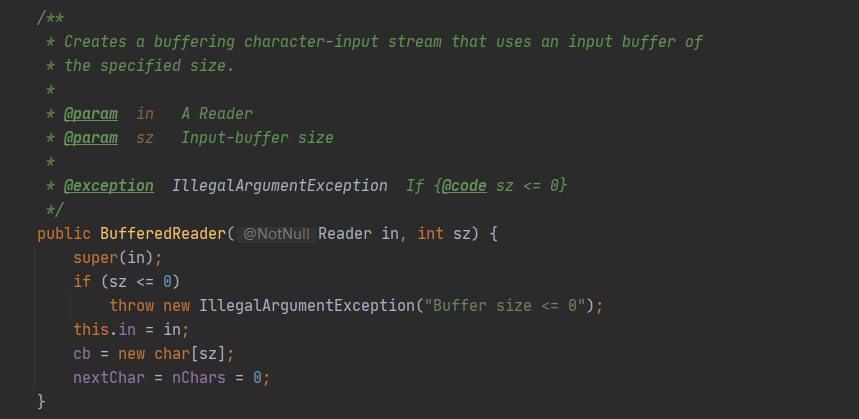
模拟修饰器设计模式
//抽象父类
public abstract class Reader_ {
public void read(){
}
}
public class BufferedReader_ extends Reader_{
private Reader_ reader_;
public BufferedReader_(Reader_ reader_) {
this.reader_ = reader_;
}
public void read() { //封装一层
reader_.read();
}
//让方法更加灵活, 多次读取文件, 或者加缓冲byte[] ....
public void readNum(int num) {
for(int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
reader_.read();
}
}
}
public class FileReader_ extends Reader_{
public void read(){
System.out.println("读取文件");
}
}
public class StringReader_ extends Reader_{
public void read(){
System.out.println("文件转字符串");
}
}
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferedReader_ bufferedReader_ = new BufferedReader_(new FileReader_());
bufferedReader_.read(); //读取文件
BufferedReader_ bufferedReader_1 = new BufferedReader_(new StringReader_());
bufferedReader_1.read(); // 文件转字符串
}
}
1.5.3 处理流的功能主要体现在以下两个方面

1.5.4 处理流-BufferedReader和BufferedWriter


BufferedReader
public class BufferedReader_ {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String filePath = "e:\\a.java";
//创建bufferedReader
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filePath));
//读取
String line; //按行读取, 效率高
//说明
//1. bufferedReader.readLine() 是按行读取文件
//2. 当返回null 时,表示文件读取完毕
while ((line = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
//关闭流, 这里注意,只需要关闭 BufferedReader ,因为底层会自动的去关闭 节点流
//FileReader。
/*
public void close() throws IOException {
synchronized (lock) {
if (in == null)
return;
try {
in.close();//in 就是我们传入的 new FileReader(filePath), 关闭了.
} finally {
in = null;
cb = null;
}
}
}
*/
bufferedReader.close();
}
}
BufferedWriter
public class BufferedWriter_ {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String filePath = "e:\\ok.txt";
//创建BufferedWriter
//说明:
//1. new FileWriter(filePath, true) 表示以追加的方式写入
//2. new FileWriter(filePath) , 表示以覆盖的方式写入
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(filePath));
bufferedWriter.write("hello, 韩顺平教育!");
bufferedWriter.newLine();//插入一个和系统相关的换行
bufferedWriter.write("hello2, 韩顺平教育!");
bufferedWriter.newLine();
bufferedWriter.write("hello3, 韩顺平教育!");
bufferedWriter.newLine();
//说明:关闭外层流即可 , 传入的 new FileWriter(filePath) ,会在底层关闭
bufferedWriter.close();
}
}
1.5.5 BufferedReader和BufferedWriter拷贝
public class BufferedCopy_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//老韩说明
//1. BufferedReader 和 BufferedWriter 是安装字符操作
//2. 不要去操作 二进制文件[声音,视频,doc, pdf ], 可能造成文件损坏
//BufferedInputStream
//BufferedOutputStream
String srcFilePath = "e:\\a.java";
String destFilePath = "e:\\a2.java";
// String srcFilePath = "e:\\0245_韩顺平零基础学Java_引出this.avi";
// String destFilePath = "e:\\a2韩顺平.avi";
BufferedReader br = null;
BufferedWriter bw = null;
String line;
try {
br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(srcFilePath));
bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(destFilePath));
//说明: readLine 读取一行内容,但是没有换行
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
//每读取一行,就写入
bw.write(line);
//插入一个换行
bw.newLine();
}
System.out.println("拷贝完毕...");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//关闭流
try {
if(br != null) {
br.close();
}
if(bw != null) {
bw.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
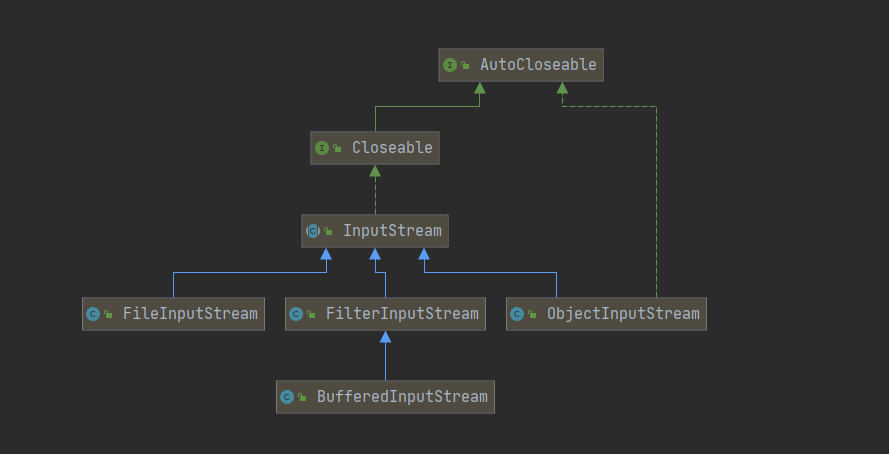
1.5.6 处理流-BufferedInputStream 和 BufferedOutputStream
BufferedInputStream
BufferedInputStream为另一个输入流添加了功能,即缓冲输入和支持mark和reset方法的功能。 当创建BufferedInputStream时,将创建一个内部缓冲区数组。 当从流中读取或跳过字节时,内部缓冲区将根据需要从所包含的输入流中重新填充,一次有多个字节。mark操作会记住输入流中的一点,并且reset操作会导致从最近的mark操作之后读取的所有字节在从包含的输入流中取出新的字节之前重新读取。

BufferedOutputStream

1.5.7BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream拷贝
BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream拷贝基于字节流
BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream = null;
BufferedOutputStream bufferedOutputStream = null;
try {
bufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(new File("C:\\Users\\asus\\Desktop\\b\\05.简历辅导-技能清单-内容-JDBC+JavaWeb.ai")));
bufferedOutputStream = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(new File("C:\\Users\\asus\\Desktop\\b\\简历辅导.ai")));
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int read = 0;
while ((read = bufferedInputStream.read(bytes)) != -1) {
//读多少写多少
bufferedOutputStream.write(bytes, 0, read);
}
System.out.println("文件拷贝完毕~~~");
} catch (IOException e) {
String s = ExceptionUtils.readStackTrace(e);
System.out.println(s);
} finally {
try {
if (bufferedInputStream != null) {
bufferedInputStream.close();
}
if (bufferedOutputStream != null) {
bufferedOutputStream.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
1.5.8对象流-ObjectInputStream和ObjectOutputStream

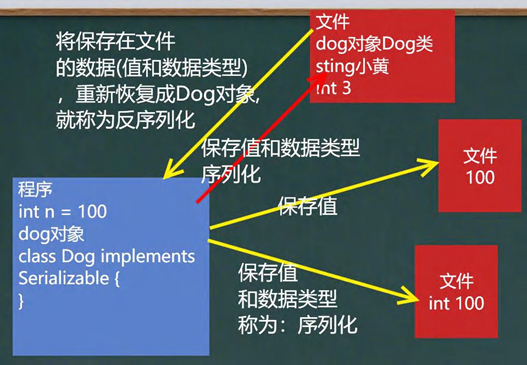
ObjectInputStream
public class ObjectInputStream_ {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
//指定反序列化的文件
String filePath = "e:\\data.dat";
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(filePath));
//读取
//老师解读
//1. 读取(反序列化)的顺序需要和你保存数据(序列化)的顺序一致
//2. 否则会出现异常
System.out.println(ois.readInt());
System.out.println(ois.readBoolean());
System.out.println(ois.readChar());
System.out.println(ois.readDouble());
System.out.println(ois.readUTF());
//dog 的编译类型是 Object , dog 的运行类型是 Dog
Object dog = ois.readObject();
System.out.println("运行类型=" + dog.getClass());
System.out.println("dog信息=" + dog);//底层 Object -> Dog
//这里是特别重要的细节:
//1. 如果我们希望调用Dog的方法, 需要向下转型
//2. 需要我们将Dog类的定义,放在到可以引用的位置
Dog dog2 = (Dog)dog;
System.out.println(dog2.getName()); //旺财..
//关闭流, 关闭外层流即可,底层会关闭 FileInputStream 流
ois.close();
}
}
ObjectOutputStream
public class ObjectOutStream_ {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//序列化后,保存的文件格式,不是存文本,而是按照他的格式来保存
String filePath = "e:\\data.dat";
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(filePath));
//序列化数据到 e:\data.dat
oos.writeInt(100);// int -> Integer (实现了 Serializable)
oos.writeBoolean(true);// boolean -> Boolean (实现了 Serializable)
oos.writeChar('a');// char -> Character (实现了 Serializable)
oos.writeDouble(9.5);// double -> Double (实现了 Serializable)
oos.writeUTF("韩顺平教育");//String
//保存一个dog对象
oos.writeObject(new Dog("旺财", 10, "日本", "白色"));
oos.close();
System.out.println("数据保存完毕(序列化形式)");
}
}
Dog
//如果需要序列化某个类的对象,实现 Serializable
public class Dog implements Serializable {
private String name;
private int age;
//序列化对象时,默认将里面所有属性都进行序列化,但除了static或transient修饰的成员
private static String nation;
private transient String color;
//序列化对象时,要求里面属性的类型也需要实现序列化接口
private Master master = new Master();
//serialVersionUID 序列化的版本号,可以提高兼容性
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public Dog(String name, int age, String nation, String color) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.color = color;
this.nation = nation;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Dog{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", color='" + color + '\'' +
'}' + nation + " " +master;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
1.5.9对象流介绍
功能:提供了对基本类型或对象类型的序列化和反序列化的方法
ObjectOutputStream提供序列化功能
ObjectInputStream提供反序列化功能
易错点
读写顺序一致,举例当有多个读写时,ois.readInt()和oos.writeInt(100);的读写顺序要一致
添加serialVersionUID之后,当Dog类中添加了字段或者方法时,底层不会认为是一个新的对象而只会认为对象被修改了。
添加serialVersionUID一方面提高了兼容性也提高了效率

1.5.10 标准输入输出流


public class InputAndOutput {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//System 类 的 public final static InputStream in = null;
// System.in 编译类型 InputStream
// System.in 运行类型 BufferedInputStream
// 表示的是标准输入 键盘
System.out.println(System.in.getClass());
//1. System.out public final static PrintStream out = null;
//2. 编译类型 PrintStream
//3. 运行类型 PrintStream
//4. 表示标准输出 显示器
System.out.println(System.out.getClass());
System.out.println("hello, 韩顺平教育~");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("输入内容");
String next = scanner.next();
System.out.println("next=" + next);
}
}
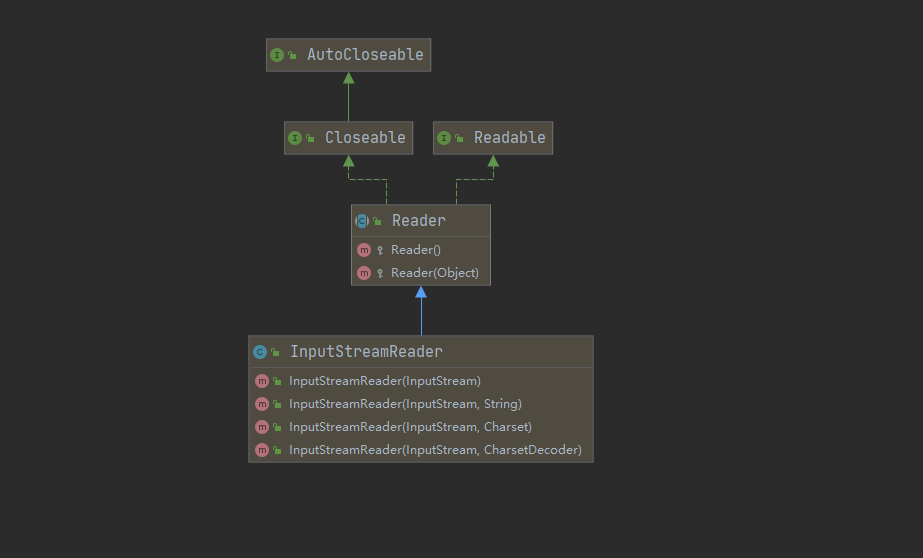
1.5.11 转换流-InputStreamReader 和 OutputStreamWriter
从文件乱码问题,引出学习转行流必要性
InputStreamReader
OutputStreamWriter
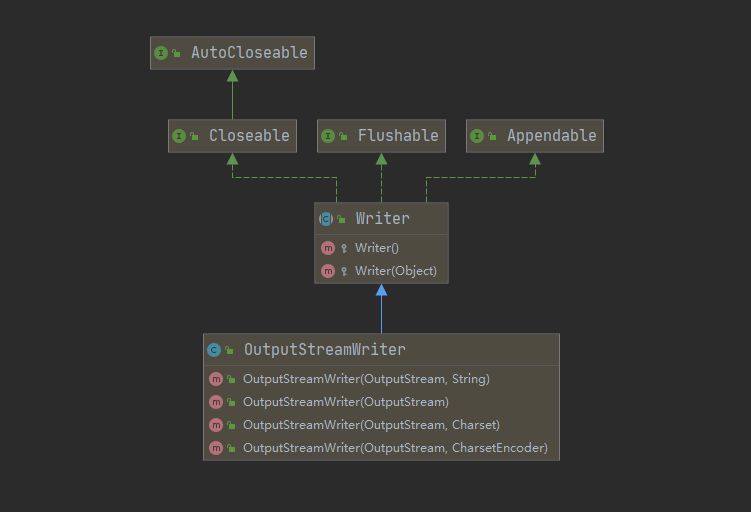
OutputStreamWriter和InputStreamReader中如果没有指定字符集则默认为UTF-8
OutputStreamWriter和InputStreamReader是字符流适用于纯文本文件,不适用于视频、音频、word、pdf等文件
public static Charset defaultCharset() {
if (defaultCharset == null) {
synchronized (Charset.class) {
String csn = AccessController.doPrivileged(
new GetPropertyAction("file.encoding"));
Charset cs = lookup(csn);
if (cs != null)
defaultCharset = cs;
else
defaultCharset = forName("UTF-8");
}
}
return defaultCharset;
}

示例
public class CodeQuestion {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//OutputStreamWriter和InputStreamReader中如果没有指定字符集则默认为UTF-8
String filePath = "C:\\Users\\asus\\Desktop\\b\\code.txt";
OutputStreamWriter outputStreamWriter = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(new File(filePath)),"gbk");
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(outputStreamWriter);
bufferedWriter.write("超级赛亚人!\nsun guKong~");
bufferedWriter.close();
InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(new File(filePath)));
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(inputStreamReader);
String readLine = null;
while ((readLine = bufferedReader.readLine())!=null){
System.out.println(readLine);
}
bufferedReader.close();
}
}
1.5.12 打印流-PrintStream和PrintWriter

打印流既可以输出到控制台也可以写入到文件中
PrintWriter
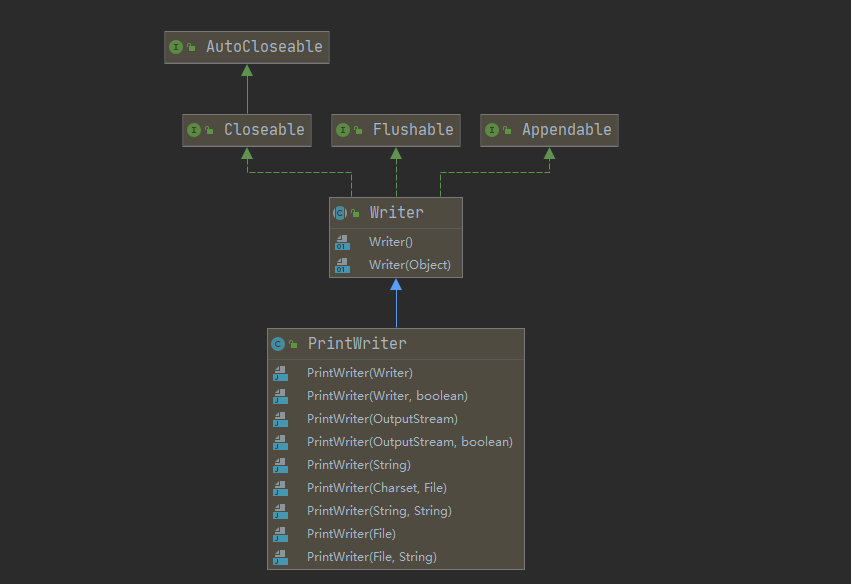
public class PrintWriter_ {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//输出到控制台
PrintWriter printWriter = new PrintWriter(System.out);
//写入文件
// PrintWriter printWriter = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter("e:\\f2.txt"));
printWriter.print("hi, 北京你好~~~~");
printWriter.close();//flush + 关闭流, 才会将数据写入到文件..
}
}
PrintStream
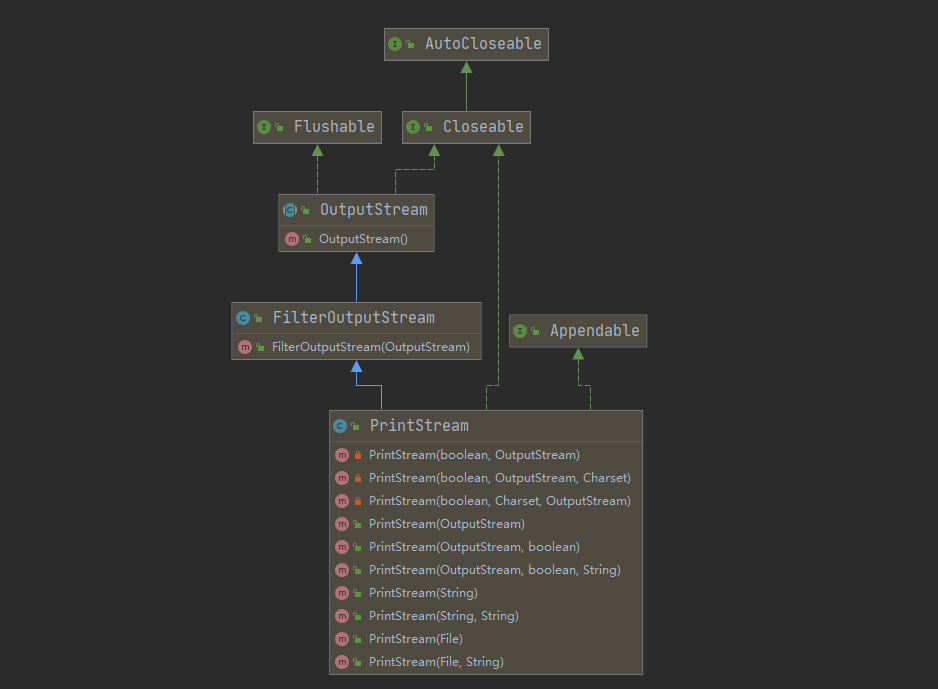
public class PrintStream_ {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
PrintStream out = System.out;
//在默认情况下,PrintStream 输出数据的位置是 标准输出,即显示器
/*
public void print(String s) {
if (s == null) {
s = "null";
}
write(s);
}
*/
out.print("john, hello");
//因为print底层使用的是write , 所以我们可以直接调用write进行打印/输出
out.write("韩顺平,你好".getBytes());
out.close();
//我们可以去修改打印流输出的位置/设备
//1. 输出修改成到 "e:\\f1.txt"
//2. "hello, 韩顺平教育~" 就会输出到 e:\f1.txt
//3. public static void setOut(PrintStream out) {
// checkIO();
// setOut0(out); // native 方法,修改了out
// }
// System.setOut(new PrintStream("e:\\f1.txt"));
System.out.println("hello, 韩顺平教育~");
}
}
1.5.13 Properties类
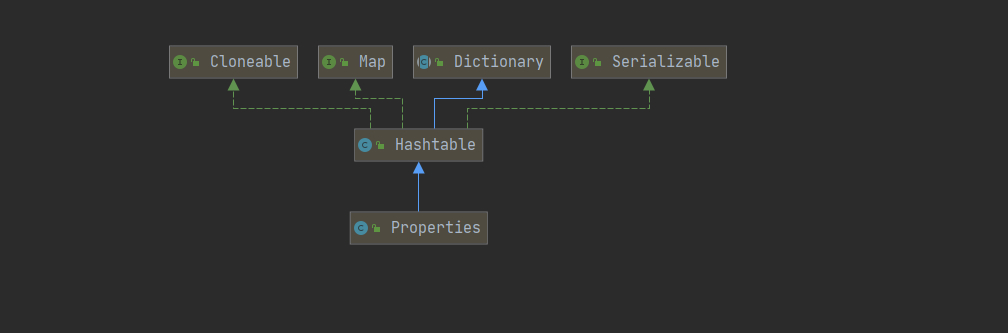
看一个需求,配置文件引出Properties

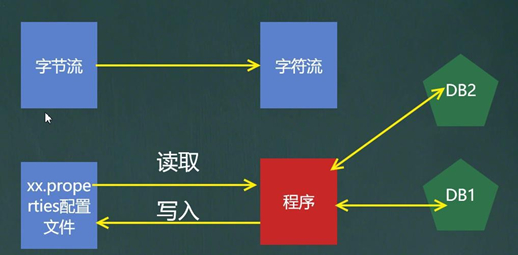
通过字符流或者字节流取出配置文件中的数据,随用可以实现功能但是会非常麻烦
public class Properties01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String filePath = "C:\\ide\\IdeaProjects\\llp-javase\\javacode\\chapter19\\mysql.properties";
//这里mysql.properties为纯文件可以使用字节流和字符流均可,但是字符流效率会更高一些
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(new File(filePath))));
String readLine = null;
while ((readLine = bufferedReader.readLine())!= null){
String[] split = readLine.split("=");
//取出用户名
for (int i = 0; i < split.length; i++) {
if("username".equals(split[i])){
//username的值是llp
System.out.println(split[i]+"的值是"+split[i+1]);
}
}
}
}
}


通过Properties读取配置文件中的数据
public class Properties02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//使用Properties 类来读取mysql.properties 文件
//1. 创建Properties 对象
Properties properties = new Properties();
//2. 加载指定配置文件
String filePath = "C:\\ide\\IdeaProjects\\llp-javase\\javacode\\chapter19\\mysql.properties";
properties.load(new FileReader(filePath));
//3. 把k-v显示控制台
properties.list(System.out);
//4. 根据key 获取对应的值
String user = properties.getProperty("username");
String pwd = properties.getProperty("password");
System.out.println("用户名=" + user);
System.out.println("密码是=" + pwd);
}
}
通过properties将数据写入配置文件中
public class Properties03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//使用Properties 类来创建 配置文件, 修改配置文件内容
Properties properties = new Properties();
//创建
//1.如果该文件没有key 就是创建
//2.如果该文件有key ,就是修改
/*
Properties 父类是 Hashtable , 底层就是Hashtable 核心方法
public synchronized V put(K key, V value) {
// Make sure the value is not null
if (value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
// Makes sure the key is not already in the hashtable.
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> entry = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
for(; entry != null ; entry = entry.next) {
if ((entry.hash == hash) && entry.key.equals(key)) {
V old = entry.value;
entry.value = value;//如果key 存在,就替换
return old;
}
}
addEntry(hash, key, value, index);//如果是新k, 就addEntry
return null;
}
*/
properties.setProperty("charset", "utf8");
properties.setProperty("user", "汤姆");//注意保存时,是中文的 unicode码值
properties.setProperty("pwd", "888888");
//将k-v 存储文件中即可
properties.store(new FileOutputStream("src\\mysql2.properties"), null);
System.out.println("保存配置文件成功~");
}
}
 JavaSE
JavaSE
 JavaWeb
JavaWeb
 Spring
Spring
 MyBatis
MyBatis
 linux
linux
 消息队列
消息队列
 工具
工具
 片段
片段
 AI
AI
 搜索
搜索